9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:敲除 circRAD18 可以通过调节 miR-613/HK2 轴减轻乳腺癌的进展
Authors Zang H, Li Y, Zhang X, Huang G
Received 21 December 2019
Accepted for publication 29 April 2020
Published 19 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3661—3672
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S243300
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lu-Zhe Sun
***本文章已被撤回***
Background: Breast cancer (BC) remains the most prevalent malignancy and the leading cause of cancer death. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been discovered to serve as crucial regulators in BC. In the current work, we aimed to study the impact of circRAD18 (hsa_circ_0002453) on BC progression and mechanism governing it.
Materials and Methods: The expression levels of circRAD18, miR-613 and hexokinase 2 (HK2) mRNA were determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). CircRAD18 identification was performed using RNase R digestion and actinomycin D assay. Cell viability, colony formation, apoptosis, migration, invasion and glycolysis were measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, colony formation assay, flow cytometry, transwell analysis and extracellular acidification rate detection assay, respectively. Western blot was used to assess the levels of E-Cadherin, Vimentin, N-Cadherin and HK2 protein. The targeted interplay between miR-613 and circRAD18 or HK2 was detected by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Xenograft model assay was performed to observe the role of circRAD18 in vivo.
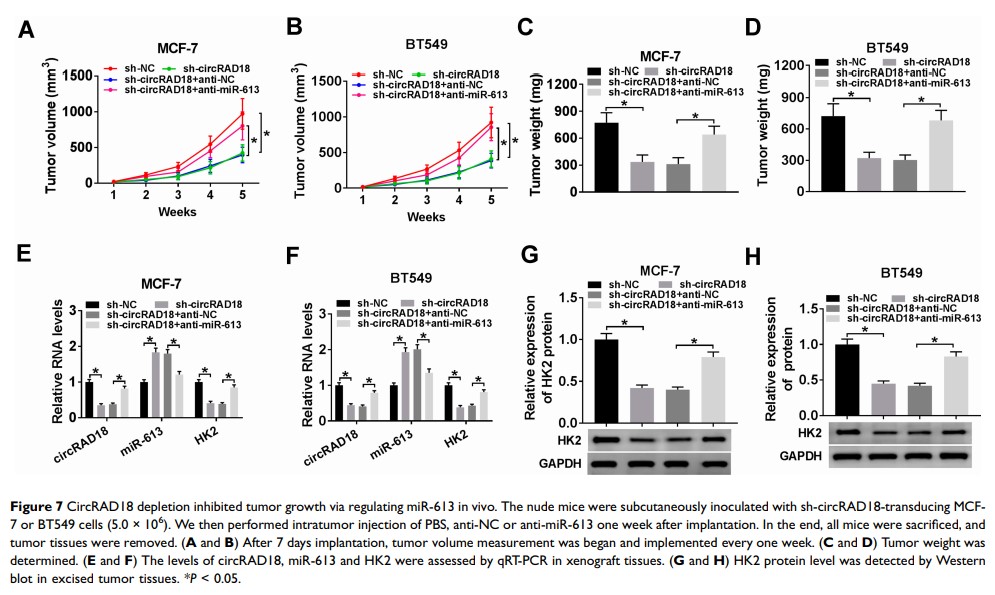
Results: CircRAD18 was highly expressed in BC tissues and cells. CircRAD18 depletion hindered BC cell malignant behaviors, as evidenced by the inhibition in cell viability, colony formation, migration, invasion, epithelial to mesenchymal transition and glycolysis, as well as the promotion in cell apoptosis. CircRAD18 directly interacted with miR-613, and miR-613 mediated the repressive effect of circRAD18 knockdown on BC cell malignant behaviors. Moreover, HK2 was a direct target of miR-613, and circRAD18 positively regulated HK2 expression via sponging miR-613. Additionally, circRAD18 knockdown repressed tumor growth in vivo by miR-613.
Conclusion: Our current work suggested that circRAD18 silencing suppressed BC cell malignant behaviors in vitro and tumor growth in vivo at least partly via the regulation of the miR-613/HK2 axis, highlighting that circRAD18 might be a promising therapeutic target for BC treatment.
Keywords: BC, circRAD18, miR-613, HK2, malignant behaviors