9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

T1-2 期非小细胞肺癌患者的手术依从性和生存结果
Authors Wang S, Mao W, Wang Y, Shi X, Wang W, Dai L, Zhang W
Received 15 November 2019
Accepted for publication 27 April 2020
Published 19 May 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 3597—3610
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S238819
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Introduction: Our aim was to determine the relationship between surgical compliance and survival outcomes in patients with stage T1-2 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Patients with T1-2 NSCLC who were diagnosed between 2004 and 2015 were identified from the SEER database. Multivariate logistic regression was used to analyse factors associated with surgical compliance. Kaplan–Meier curves and Cox regression were used to analyse the effects of surgical compliance on overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS).
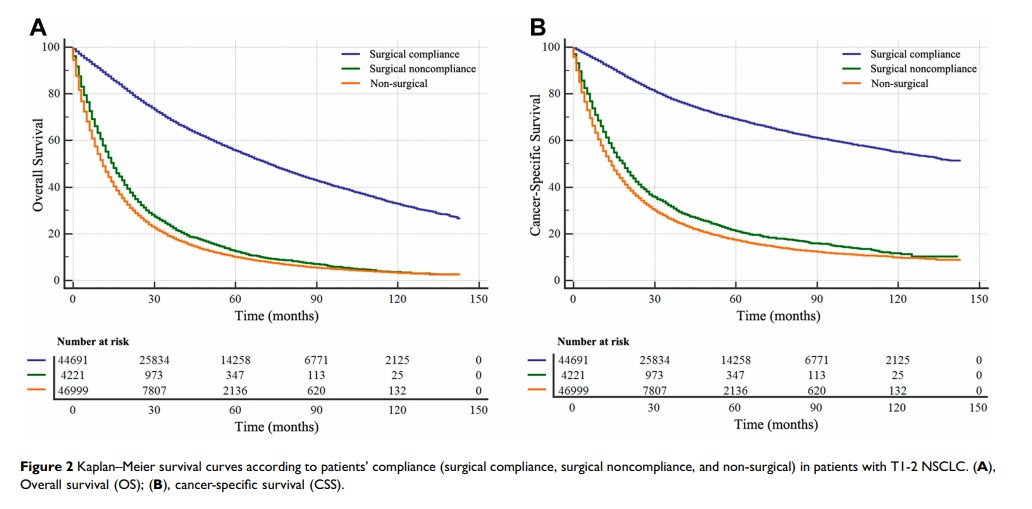
Results: Of the 221,704 eligible T1-2 NSCLC patients, 106,668 patients recommended surgery. Among them, 99,672 (93.4%) patients were surgical compliance group, and 6996 (6.6%) were surgical noncompliance group. Poor surgical compliance was associated with earlier diagnosis time, old age, male, black race, unmarried status, main bronchus site, poor grade/stage, and lower household income. Patients’ compliance was an independent prognostic factor for OS and CSS of T1-2 NSCLC patients. Multivariate Cox regression showed that surgical noncompliance individuals showed lower OS (hazard ratio [HR] 2.494; 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.423– 2.566, p < 0.001) and lower CSS (HR 2.877; 95% CI 2.782– 2.974, p < 0.001) compared with surgical compliance patients. In addition, results in the non-surgical group were observed to be similar to those of the surgical noncompliance group.
Conclusion: We found that patients’ compliance was an independent prognostic factor for survival in T1-2 NSCLC patients. Poor surgical compliance was associated with earlier diagnosis time, old age, male, black race, unmarried status, main bronchus site, poor grade/stage, and lower household income.
Keywords: non-small-cell lung cancer, surgical compliance, survival outcome, SEER