9 0 4 9 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

中性粒细胞-淋巴细胞比(NLR)预测冠状动脉疾病和 2 型糖尿病患者的临床疗效: 倾向评分匹配分析
Authors Qiao S, Gao W, Guo S
Received 3 January 2020
Accepted for publication 3 April 2020
Published 19 May 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 437—443
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S244623
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) combined with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) frequently occurred. In this study, we aimed at exploring the prognostic significance of blood neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in these types of patients.
Patients and Methods: Between June 30, 2010 and August 30, 2017, 1454 patients with CVD were enrolled in this study. Kaplan and Meier methodology was used for survival analysis. We also used propensity score matching (PSM) to further compare survival in patients with or without T2DM.
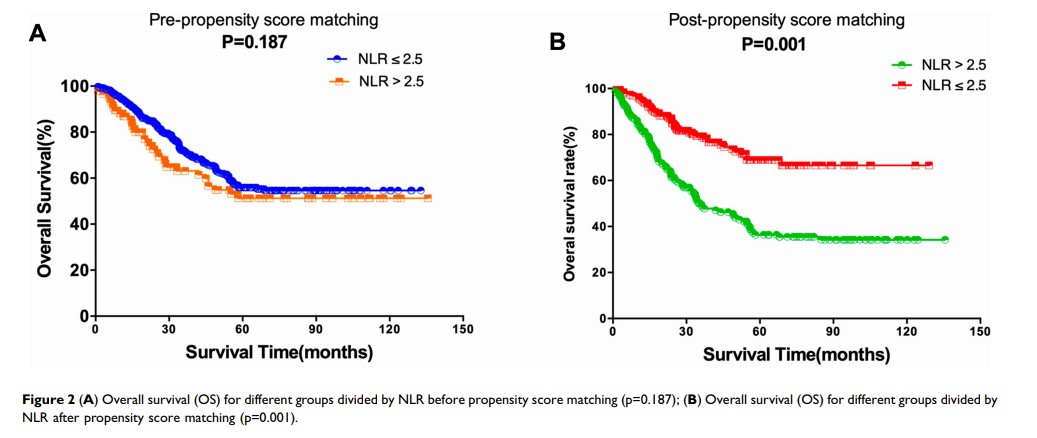
Results: Among all patients, we applied ROC curve analysis to stratify all patients into two different groups including NLR > 2.5 (n=432) and NLR≤ 2.5 (n=1022) groups. After that, we further performed survival analysis between different groups. We found that patients with NLR ≤ 2.5 had significantly favorable OS compared with the overall survival in patients with NLR > 2.5. We further built the PSM using 242 pairs of patients who have CVD and with or without T2DM. After adjusting for competing risk factors, we performed Cox proportional hazards models to identify the independent prognostic factors in multivariable adjustment. We found that NLR ≤ 2.5 (HR: 2.576, 95% CI: 1.241– 4.583, P =0.001) and extent of coronary artery disease (HR: 2.432, 95% CI: 1.189– 4.392, P =0.005) remained independent predictors of OS.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we have established an PSM model and found that a high NLR value was an independent prognostic factor for survival, predicting in patients with both CAD and T2DM. The NLR value would be a valuable biomarker to evaluate the outcomes of patients and give them opportunities for choosing alternative therapies.
Keywords: neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio, NLR, cardiovascular diseases, CVD, type 2 diabetes mellitus, T2DM