9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

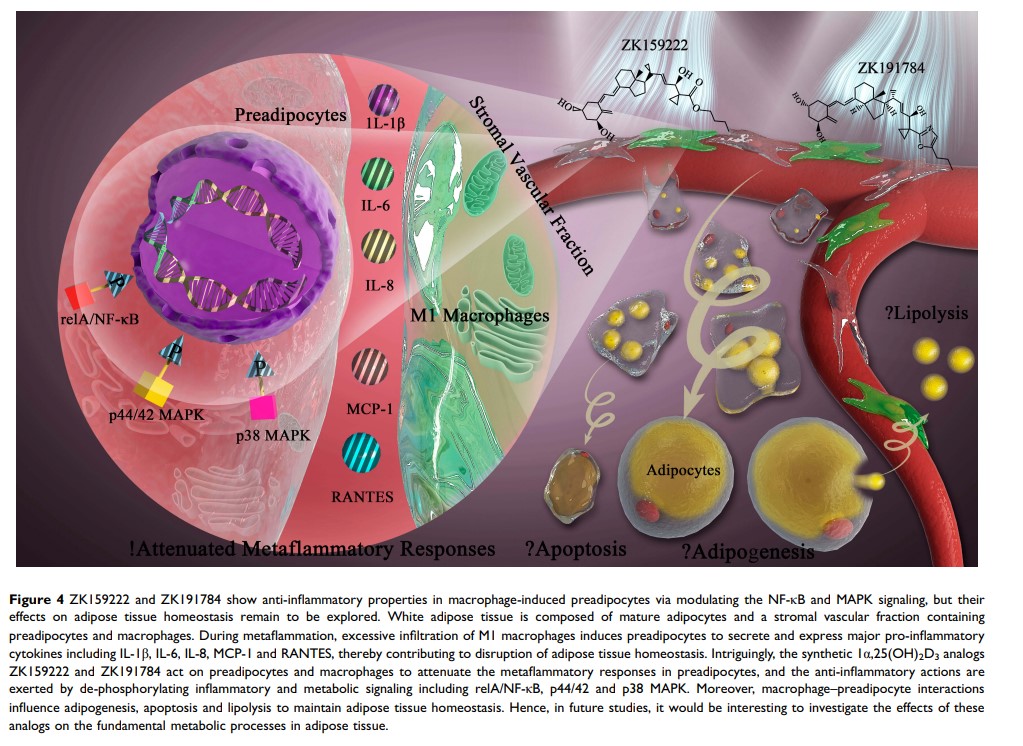
1α,25(OH)2D3 类似物 ZK159222 和 ZK191784 通过调节 NF-κB 和 MAPK 信号传导在巨噬细胞诱导的前脂肪细胞中显示抗炎特性
Authors Zhu J, Wilding JPH
Received 10 January 2020
Accepted for publication 3 April 2020
Published 19 May 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1715—1724
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S245080
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonio Brunetti
Purpose: Key research findings suggest that attenuating metaflammation in adipose tissue might be a strategic step to prevent the metabolic syndrome and its associated disease outcomes. The anti-inflammatory effects of 1α,25(OH)2D3 have been confirmed in our previous studies, but adverse effects induced at high concentrations restrict its potential clinical translation. Two synthetic 1α,25(OH)2D3 analogs ZK159222 and ZK191784 have manifested promising tissue-specific immunomodulatory actions, but limited data are available on adipose tissue. Hence, in this study, we investigated whether ZK159222 and ZK191784 act on preadipocytes or macrophages to attenuate metaflammatory responses via modulating inflammatory and metabolic signaling in macrophage-induced preadipocytes.
Methods: Preadipocyte-specific effects of ZK159222 and ZK191784 on macrophage-induced preadipocytes were tested by pre-incubating and incubating preadipocytes with the analogs and MacCM. Separately, macrophage-specific effects of both analogs on macrophage-induced preadipocytes were tested by incubating preadipocytes with analog-MacCM or MacCM. The effects of 1α,25(OH)2D3 were also examined and set as the positive control. Metaflammatory responses were determined as the concentrations and gene expression of major pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1 and RANTES, measured using ELISA and qPCR. Inflammatory and metabolic signaling including NF-κB and MAPK were probed using Western blotting.
Results: ZK159222 and ZK191784 act on preadipocytes and macrophages to decrease the secretion and gene expression of the major pro-inflammatory cytokines in macrophage-induced preadipocytes. The anti-inflammatory effects were at least as potent as 1α,25(OH)2D3, and no preadipocyte apoptosis was induced at high concentrations. In addition, mostly at high concentrations, both analogs moderately decreased the phosphorylation of relA, p44/42 and p38 MAPK in macrophage-induced preadipocytes.
Conclusion: ZK159222 and ZK191784 act on macrophages and preadipocytes to attenuate metaflammatory responses in macrophage-induced preadipocytes, by decreasing phosphorylation of relA/NF-κB, p44/42 and p38 MAPK.
Keywords: vitamin D, metaflammatory response, relA, p44/42, p38