9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

指导聚合物胶束的适当辐照时间,以最大程度提高化学-光动力治疗的效果
Authors Zhu Y, Yu F, Tan Y, Wen L, Li Y, Yuan H, Hu F
Received 1 April 2020
Accepted for publication 13 July 2020
Published 31 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 6531—6543
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S256477
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
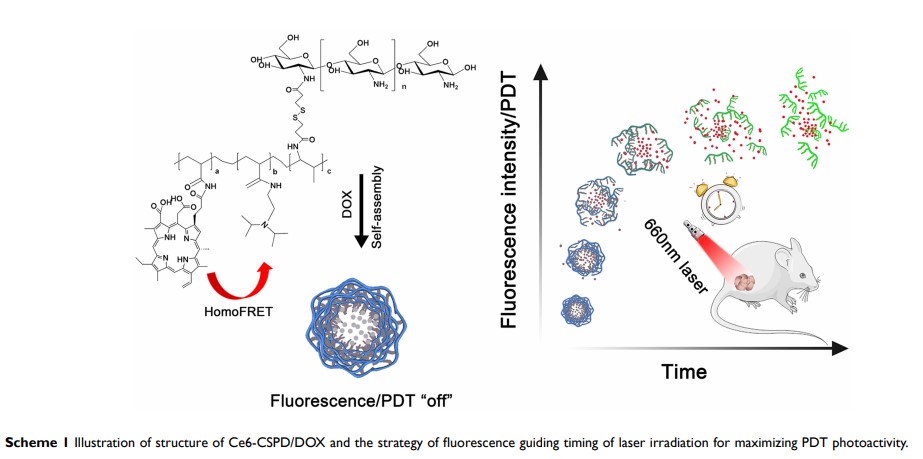
Background: Photoactivity “on-off” switchable nano-agents could shield phototoxicity until reaching target region, which immensely promoted photodynamic therapy. However, the masking ratio of nano-agents in vivo was dynamic and positively correlated with the phototoxicity induced by laser irradiation, in which case the timing of laser irradiation was unpredictable to maximize antitumor efficacy.
Methods: Herein, low molecular weight chitosan and hydrophobic polymethylacrylamide derivatives were linked via GSH cleavable 3, 3ʹ-dithiodipropionic acid to construct polymeric micelles (Ce6-CSPD). The doxorubicin loading nano-agent (Ce6-CSPD/DOX) could quench both photoactivity and fluorescence of photosensitizer chlorin e6 (Ce6) and doxorubicin (DOX) under physiological condition by homo-fluorescence resonance energy transfer (homoFRET).
Results: Once internalized by tumor cells, the photoactivity as well as fluorescence of Ce6 was recovered rapidly when motivated by intracellular high GSH. Specifically, the fluorescence intensity and photoactivity of Ce6 were proven to be positive linear correlated, upon which appropriate timing of laser irradiation could be determined by referring to the dynamic fluorescence intensity in vivo. In addition, the theranostic nano-agents also possessed the capacity of monitoring the DOX release process. Accordingly, under the guidance of fluorescence intensity, the experimental group subjected to laser irradiation at 18 h postadministration acquired the highest antitumor inhibition efficacy compared to that at four hours and 48 h, which held great potential for maximizing chemo-photodynamic therapy and avoiding nonspecific phototoxicity precisely to normal organs.
Conclusion: In summary, we prepared homoFRET-based theranostic nano-agent (Ce6-CSPD/DOX) for monitoring PDT precisely and decreasing phototoxicity to normal organs before reaching target region. Under the guidance of dynamic fluorescence intensity, the appropriate laser irradiation timing could be monitored to maximize antitumor therapy efficacy, which offered opportunities for monitoring efficiency of chemo-photodynamic therapy in a timely and accurate manner.
Keywords: theranostic, photodynamic therapy, tumor, micelle