9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
一个潜在的新型药物硫化氢,减少刀豆蛋白 A 引起的肝炎
Authors Cheng P, Chen K, Xia Y, Dai WQ, Wang F, Shen M, Wang C, Yang J, Zhu R, Zhang H, Li JJ, Zheng Y, Wang J, Zhang Y, Lu J, Zhou YQ, Guo CY
Published Date September 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 1277—1286
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S66573
Received 21 April 2014, Accepted 4 June 2014, Published 9 September 2014
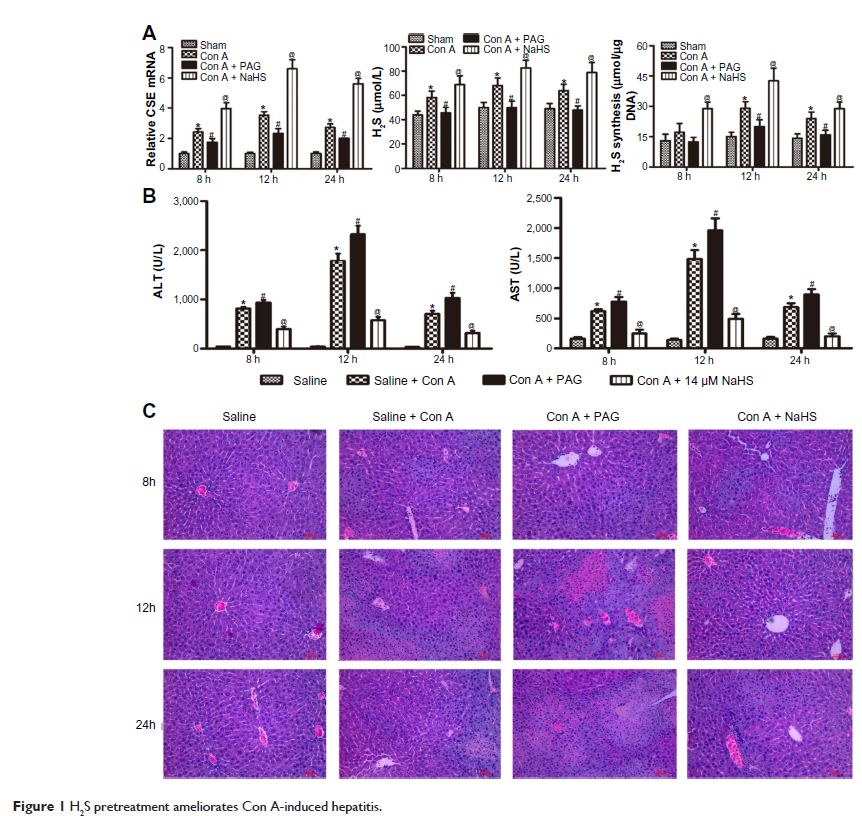
Background: Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is known to exert anti-inflammatory properties. Apoptosis and autophagy play important roles in concanavalin A (Con A)-induced acute hepatitis. The purpose of this study was to explore both the effect and mechanism of H2S on Con A-induced acute hepatitis.
Methods: BALB/c mice were randomized into sham group, Con A-injection group, and 14 µmol/kg of sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS, an H2S donor) pretreatment group.
Results: Aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and pathological damage were significantly ameliorated by NaHS pretreatment. NaHS pretreatment significantly reduced the levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α compared with those of the Con A group. The expression of Bcl-2, Bax, Beclin-1, and LC3-2, which play important roles in the apoptosis and autophagy pathways, were also clearly affected by NaHS. Furthermore, NaHS affected the p-mTOR and p-AKT.
Conclusion: H2S attenuates Con A-induced acute hepatitis by inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy, in part, through activation of the PtdIns3K-AKT1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: NaHS, apoptosis, PtdIns3K-AKT, autophagy
Methods: BALB/c mice were randomized into sham group, Con A-injection group, and 14 µmol/kg of sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS, an H2S donor) pretreatment group.
Results: Aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and pathological damage were significantly ameliorated by NaHS pretreatment. NaHS pretreatment significantly reduced the levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α compared with those of the Con A group. The expression of Bcl-2, Bax, Beclin-1, and LC3-2, which play important roles in the apoptosis and autophagy pathways, were also clearly affected by NaHS. Furthermore, NaHS affected the p-mTOR and p-AKT.
Conclusion: H2S attenuates Con A-induced acute hepatitis by inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy, in part, through activation of the PtdIns3K-AKT1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: NaHS, apoptosis, PtdIns3K-AKT, autophagy