9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

利用药物治疗 13,970 名中国女性 2 型糖尿病,血糖控制差的非药物因素:在中国四个城市的 77 所三级医院中进行的一项横断面调查研究
Authors Lu J, Weng J, Gu W, Guo X, Yang W, Zou D, Zhou Z, Zhu D, Ji Q, Ji L, Yang X
Published Date August 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 1161—1167
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S66915
Received 28 April 2014, Accepted 27 June 2014, Published 30 August 2014
Background: Achieving good glycemic control improves clinical outcomes among patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). This study aimed to explore non-pharmaceutical factors for poor glycemic control in Chinese women with T2D who used antidiabetic drug(s).
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted in March to June 2011 in 77 top tertiary hospitals in Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, and Guangzhou, People’s Republic of China (the coverage rates of the 3A hospitals: 74.4%, 76%, 55%, and 29.3%, respectively). Of 29,502 patients with T2D who used oral antidiabetic drugs (OADs) alone or combined with insulin, 13,970 were women and used in the analysis. Logistic regression analysis was used to obtain odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of factors for hyperglycemia defined as HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin) ≥77 mmol/mol (7.0%).
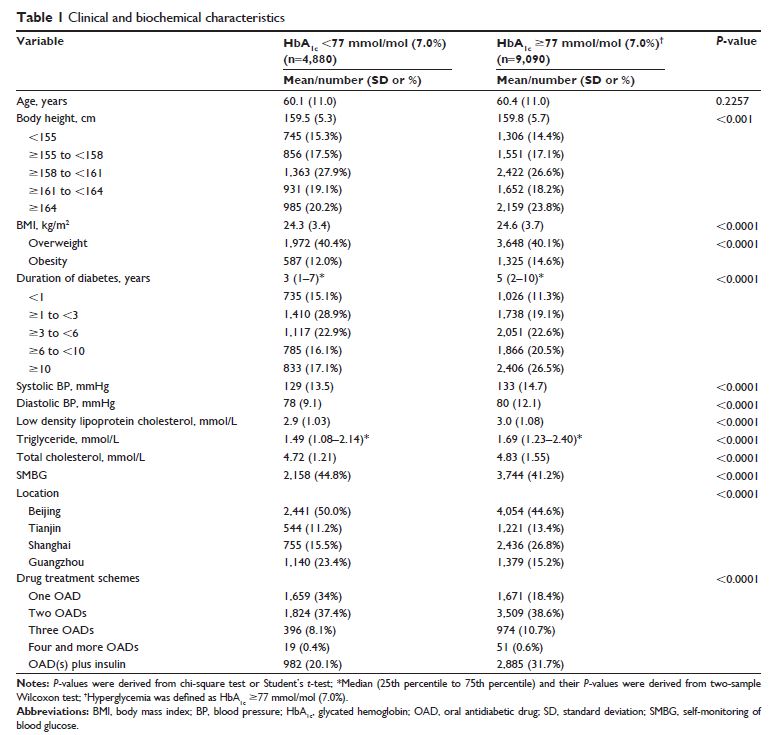
Results: The mean age was 60.3 (standard deviation 11.0) years, with a median of 4 (interquartile range 2–9) years of duration of diabetes, and 65.1% had hyperglycemia. In multivariable analysis, body height of ≥164 cm (OR 1.26, 95% CI 1.15–1.37) and obesity (OR 1.16, 95% CI 1.04–1.31) was associated with increased risk of hyperglycemia, while self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) decreased the risk of hyperglycemia (OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.73–0.84). Duration of diabetes ≥3 years (≥3 to <6 years, OR 1.46, 95% CI 1.32–1.62; ≥6 to <10 years, OR 1.65, 95% CI 1.44–1.89), especially ≥10 years (OR 1.95, 95% CI 1.73–2.19), was associated with higher risks of hyperglycemia.
Conclusion: Body height ≥164 cm, obesity, and duration of diabetes ≥3 years increased while SMBG decreased risk of hyperglycemia in Chinese women with OAD-treated T2D.
Keywords: HbA1c goal, hyperglycemia, oral antidiabetic drugs