9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
长非编码 RNA PVT1 在人类胃癌中的表达和临床意义
Authors Ding J, Li D, Gong M, Wang J, Huang X, Wu T, Wang C
Published Date September 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 1625—1630
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S68854
Received 4 June 2014, Accepted 24 July 2014, Published 18 September 2014
Approved for publication by Professor Jianmin Xu
Background: Highly sensitive markers are urgently needed for the diagnosis and grading of gastric cancer and for managing drug resistance. The recent identification of long-non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) has provided new approaches for resolving this challenge. The aim of this study was to screen and identify new biomarkers for human gastric cancer from lncRNAs.
Methods: First, we used lncRNA microarrays to conduct a preliminary screening for candidate lncRNAs of gastric cancer biomarkers in both human gastric cancer tissues and in two gastric cancer cell lines, SGC7901 cells and paclitaxel-resistant SGC7901 cells. The lncRNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1 ) was found to exhibit higher expression in both gastric cancer tissues and the SGC7901 paclitaxel-resistant cell line. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used for large-scale analysis in a large number of human gastric cancer tissues to verify the involvement of PVT1 in development of gastric cancer. The relationships between PVT1 expression and clinical features were also analyzed.
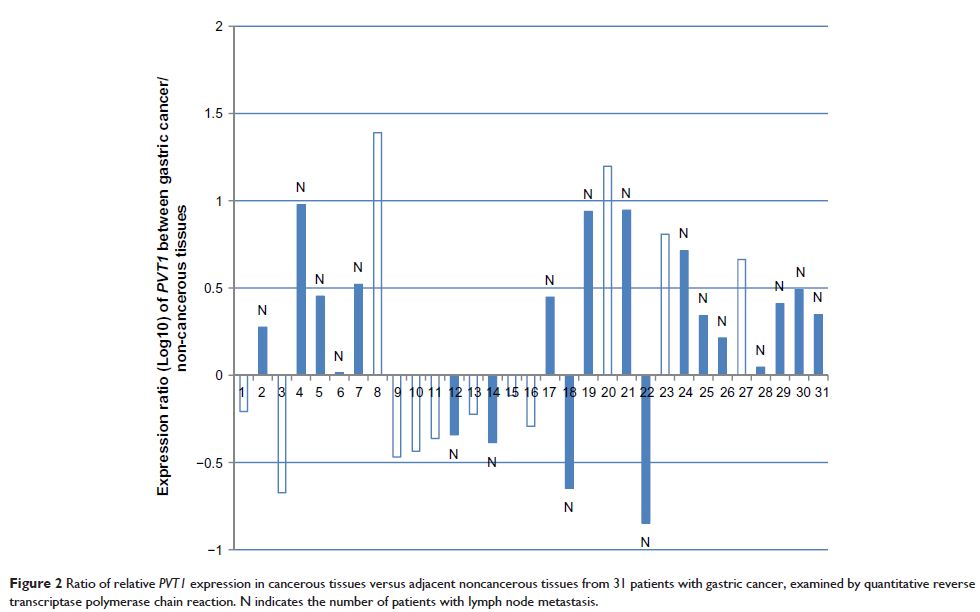
Results: PVT1 showed higher expression in human gastric cancer tissues than in adjacent non-cancerous tissues and in SGC7901 paclitaxel-resistant cells compared with SGC7901 cells. PVT1 expression was correlated with lymph node invasion of gastric cancer.
Conclusion: PVT1 is a new biomarker for human gastric cancer and may indicate lymph node invasion. Therefore, PVT1 shows potential as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of gastric cancer and enhancement of paclitaxel sensitivity.
Keywords: microarray analysis, quantitative polymerase chain reaction, lymph node invasion, tumor biomarkers, paclitaxel resistance
Methods: First, we used lncRNA microarrays to conduct a preliminary screening for candidate lncRNAs of gastric cancer biomarkers in both human gastric cancer tissues and in two gastric cancer cell lines, SGC7901 cells and paclitaxel-resistant SGC7901 cells. The lncRNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1 ) was found to exhibit higher expression in both gastric cancer tissues and the SGC7901 paclitaxel-resistant cell line. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used for large-scale analysis in a large number of human gastric cancer tissues to verify the involvement of PVT1 in development of gastric cancer. The relationships between PVT1 expression and clinical features were also analyzed.
Results: PVT1 showed higher expression in human gastric cancer tissues than in adjacent non-cancerous tissues and in SGC7901 paclitaxel-resistant cells compared with SGC7901 cells. PVT1 expression was correlated with lymph node invasion of gastric cancer.
Conclusion: PVT1 is a new biomarker for human gastric cancer and may indicate lymph node invasion. Therefore, PVT1 shows potential as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of gastric cancer and enhancement of paclitaxel sensitivity.
Keywords: microarray analysis, quantitative polymerase chain reaction, lymph node invasion, tumor biomarkers, paclitaxel resistance