9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

依据 mRNA 和 miRNA 表达谱来探索前列腺癌的分子机制
Authors Zhang X, Sun YY, Wang P, Yang CF, Li SW
Received 28 February 2017
Accepted for publication 18 May 2017
Published 29 June 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3225—3232
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S135764
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Abstract: Prostate
cancer, the second most common cancer in men, has been rarely explored by
integrating mRNA and miRNA expression profiles. In this study, we combined two
mRNA expression datasets and six documented miRNAs to uncover the comprehensive
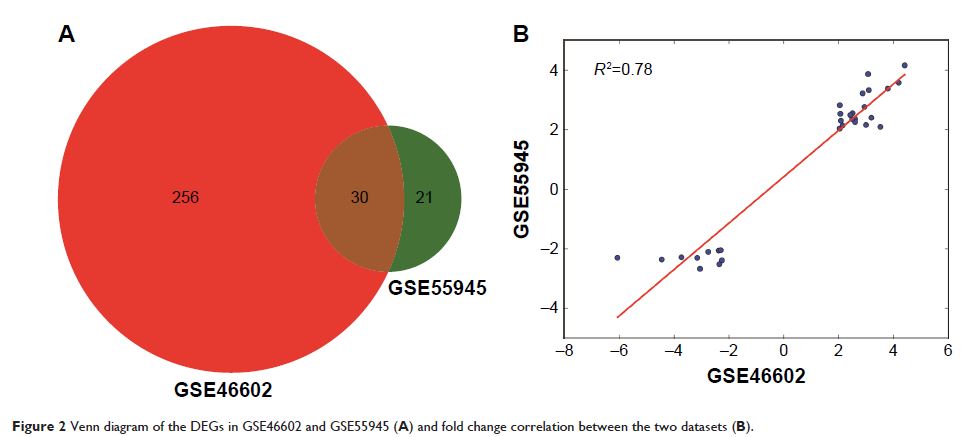
molecular mechanism of prostate cancer. Results showed that a total of 30 genes
were significantly differentially expressed in 49 tumor samples by comparing
with 22 normal samples. Importantly, all samples from the two datasets can be
clearly classified into two groups, tumor group and normal group, based on the
selected differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The miRNA–mRNA regulation
network indicated that 4 out of 30 DEGs can be regulated by three miRNAs. In
addition, prognostic performance validation using in silico databases showed
that the DEGs can significantly differentiate between low-risk and high-risk
prostate cancer. In summary, multiple biological processes are probably
involved in the development and progression of prostate cancer. First,
dysregulation of SV2 can regulate transporter and transmembrane transporter
activity and then provide the necessary nutrients for tumor cell proliferation.
Second, HOXD10 can induce cell proliferation via TCF-4. Finally, dysregulation
of CACNA1D can further suppress tumor apoptosis in prostate cancer. The
identification of critical genes and valuable biological processes can be
useful for the understanding of the molecular mechanism of prostate cancer.
Keywords: mRNA, DEGs, miRNA, prognostic