9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

姜黄素 (Curdione) 对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注损伤的神经保护作用
Authors Li XJ, Liang L, Shi HX, Sun XP, Wang J, Zhang LS
Received 11 April 2017
Accepted for publication 7 June 2017
Published 30 June 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1733—1740
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S139362
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Background: Curdione is one of the most
highly concentrated component of the active constituents in E-zhu, which has
been reported to possess a variety of activities. However, the pharmacologic
neuroprotective activity of curdione has not been evaluated. The present study
aimed to investigate the protective effect of curdione on focal cerebral
ischemia reperfusion-induced injury in rats and further exploring the
underlying mechanisms.
Materials and methods: Adult male Sprague Dawley rats were subjected to
middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) surgery for 2 h, followed by
reperfusion stage. All animals received treatment once a day for 7 days
before surgery and 14 days from 4 h after the reperfusion started.
The neurological deficit test and Morris water maze test were performed at 1,
4, 7 and 14 days after MCAO. The infarct size of animals was determined by
the 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining, and pathological brain damage
was estimated by hematoxylin–eosin staining. The malonaldehyde (MDA) levels and
the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione
peroxidase (GSH-PX) were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Expression of apoptotic proteins was measured by Western blot.
Results: Our results showed that curdione could significantly
reduce the infarct size and neurological deficits, promote cognitive function
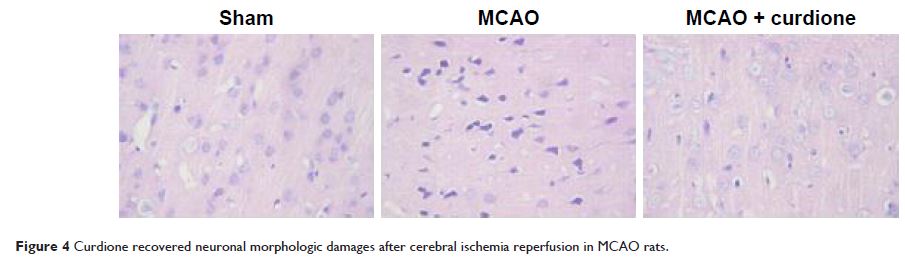
recovery and recover neuronal morphologic damages in MCAO rats. It also blocked
the increase of MDA content and elevated the activities of SOD, CAT and GSH-PX.
Moreover, curdione attenuated the expression of Cyt-C, c-caspase-3 and
c-caspase-9 increased the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and hence decreased the cellular
apoptosis.
Conclusion: Curdione possessed potential neuroprotective effect on
rats in the MCAO model. The anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic properties may be
involved in the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: curdione,
cerebral ischemia reperfusion, oxidative stress, apoptosis