9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

更正启事 — 以聚乙烯亚胺 (Polyethylenimine) 为基础的微/纳米颗粒作为疫苗佐剂
Authors Shen C, Li J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Shen G, Zhu J, Tao J
Received 25 March 2017
Accepted for publication 12 June 2017
Published 31 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5443—5460
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S137980
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Vaccines have shown great success in treating and preventing tumors and
infections, while adjuvants are always demanded to ensure potent immune
responses. Polyethylenimine (PEI), as one of the well-studied cationic
polymers, has been used as a transfection reagent for decades. However,
increasing evidence has shown that PEI-based particles are also capable of
acting as adjuvants. In this paper, we briefly review the physicochemical
properties and the broad applications of PEI in different fields, and elaborate
on the intracellular processes of PEI-based vaccines. In addition, we sum up
the proof of their in vivo and clinical applications. We also highlight some
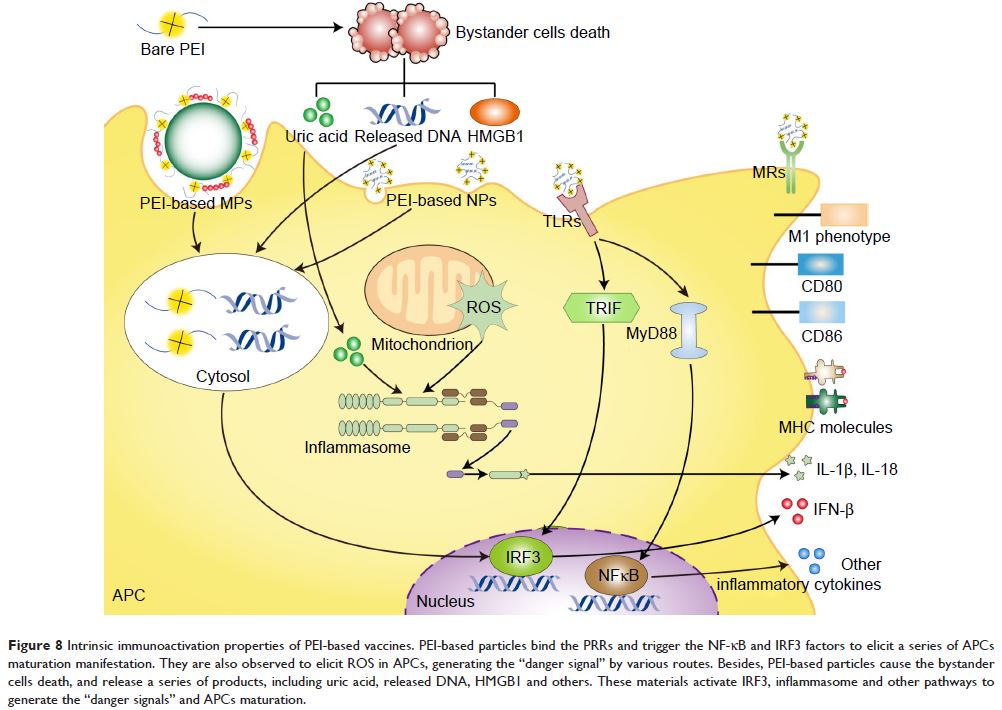
mechanisms proposed for the intrinsic immunoactivation function of PEI, followed
by the challenges and future perspectives of the applications of PEI in the
vaccines, as well as some strategies to elicit the desirable immune responses.
Keywords: cationic
polymers, APCs, immunoactivation, danger signals, anti-infection, anticancer
*作者的正确隶属单位应该包含邮政编码,如下:
Chen Shen1
Jun Li1
Yi Zhang1
Yuce Li2
Guanxin Shen3
Jintao Zhu2
Juan Tao1
1Department of
Dermatology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of
Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China; 2School of Chemistry
and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan
430074, China; 3Department of Immunology, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong
University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China