9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

R2(GFR)CHADS2 和 R2(GFR)CHA2DS2VASc 治疗方案可改善 CHADS2 和 CHA2DS2VASc 评分对中国老年房颤患者死亡风险分层的表现
Authors Fu S, Zhou S, Luo L, Ye P
Received 30 March 2017
Accepted for publication 4 May 2017
Published 8 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1233—1238
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S138405
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Zhi-Ying Wu
Background: This analysis was carried out to refine the CHADS2 and CHA2DS2VASc scores by
combining creatinine clearance (CrCl) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and
evaluate the performance of CrCl-based and GFR-based schemes in death risk
stratification of Chinese older patients with atrial fibrillation (AF).
Methods: There were 219 older patients with AF, and all-cause mortality was
assessed during the follow-up of 1.11 years. Renal function was evaluated
using the CrCl formula and different GFR (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease
[MDRD], Chinese MDRD [CMDRD], Mayo Clinic Quadratic [Mayo] and Chronic Kidney
Disease Epidemiology Collaboration [CKD-EPI]) formulas, and five kinds of R2CHADS2 and R2CHA2DS2VASc schemes were generated by combining CrCl and GFR with CHADS2 and CHA2DS2VASc scores.
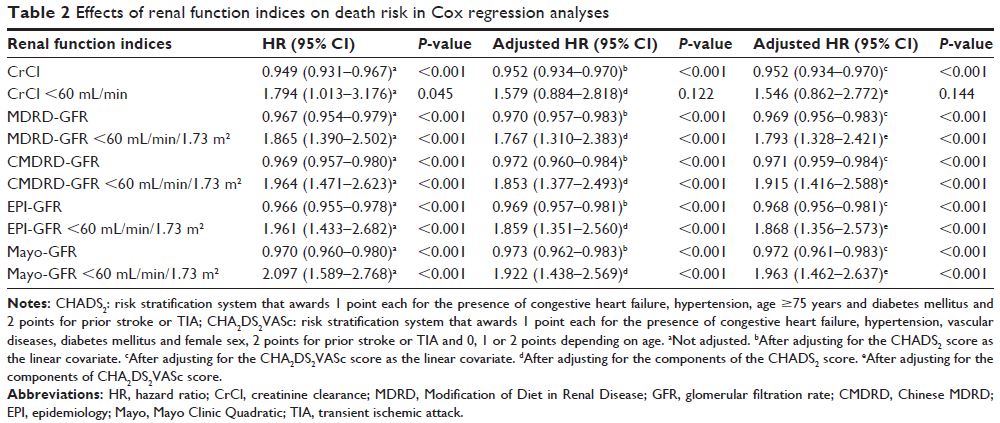
Results: In Cox regression multivariate analysis, CrCl <60 mL/min was
moderately associated with death risk (P =0.122 and P =0.144). When MDRD, CMDRD,
CKD-EPI and Mayo formulas were used to ascertain the GFR, GFR
<60 mL/min/1.73 m2 was significantly associated with death risk (P <0.001 for all). In the models
with CHADS2 and CHA2DS2VASc scores as the
linear covariates, CrCl and GFR as the continuous variables were significantly
associated with death risk (P <0.05 for all).
C-statistics of CrCl-based schemes – R2(CrCl)CHADS2 and R2(CrCl)CHA2DS2VASc – moderately exceeded that of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2VASc scores (P =0.081 and 0.082). C-statistics
of GFR-based schemes – R2(GFR)CHADS2 and R2(GFR)CHA2DS2VASc – significantly exceeded that of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2VASc scores (P <0.05 for all).
Conclusion: Chinese older patients with AF with lower levels of GFR and
GFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 had a significantly high death risk, and those with lower levels of CrCl
or CrCl <60 mL/min had a significantly or modestly high death
risk. There was significantly better performance of GFR-based schemes and
moderately better performance of CrCl-based schemes in death risk
stratification compared with CHADS2 and CHA2DS2VASc scores.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation, CHADS2, CHA2DS2VASc, older patients, creatinine clearance, glomerular filtration rate