9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

低浓度的槲皮素 (Quercetin) 拮抗人胶质母细胞瘤 U251 细胞的侵袭和血管生成
Authors Liu Y, Tang Z, Yang J, Zhou Y, Meng L, Wang H, Li C
Received 12 March 2017
Accepted for publication 6 June 2017
Published 11 August 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4023—4028
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S136821
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Narasimha Reddy Parine
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Abstract: Glioblastoma is the most
aggressive type of brain tumor with a very poor prognosis. Therefore, it is
always of great importance to explore and develop new potential treatment for
glioblastoma. Quercetin, a flavonoid present in a variety of human foods, has
been shown to inhibit various tumor cell proliferation. In this study, we found
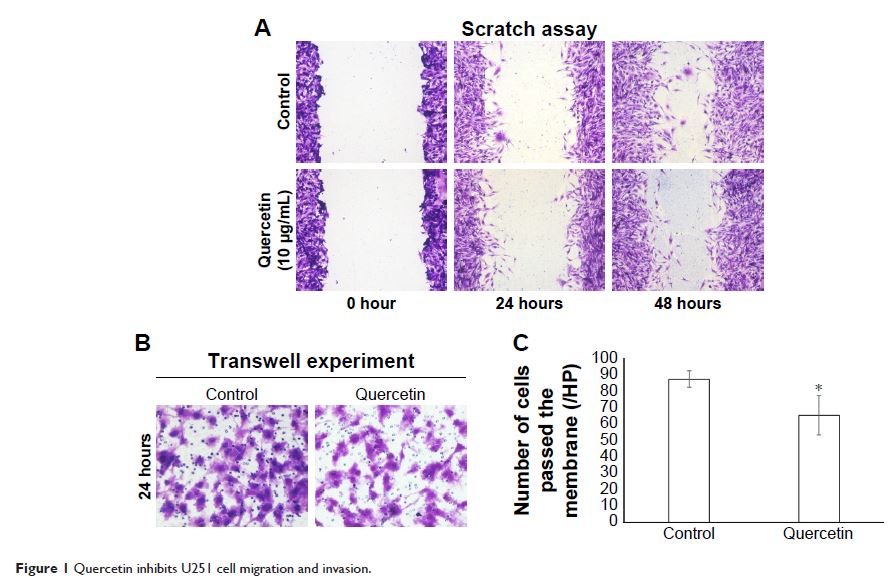
that treating human glioblastoma U251 cells with 10 µg/mL quercetin for
24 hours, a concentration that was far below the IC50 (113.65 µg/mL) and at which quercetin
failed to inhibit cell proliferation, inhibited cell migration (30%) and cell
invasion as examined by wound scratch assay and transwell assay, respectively.
We further showed that 10 µg/mL quercetin inhibited cell migration and
tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by the
conditioned medium derived from U251 cell culture. The inhibitory effect of
quercetin on migration and angiogenesis is possibly mediated through the
downregulation of protein levels of VEGFA, MMP9, and MMP2 as detected by
Western blot. Our findings demonstrated that low concentration of quercetin
antagonized glioblastoma cell invasion and angiogenesis in vitro.
Keywords: glioblastoma,
quercetin, angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis