9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

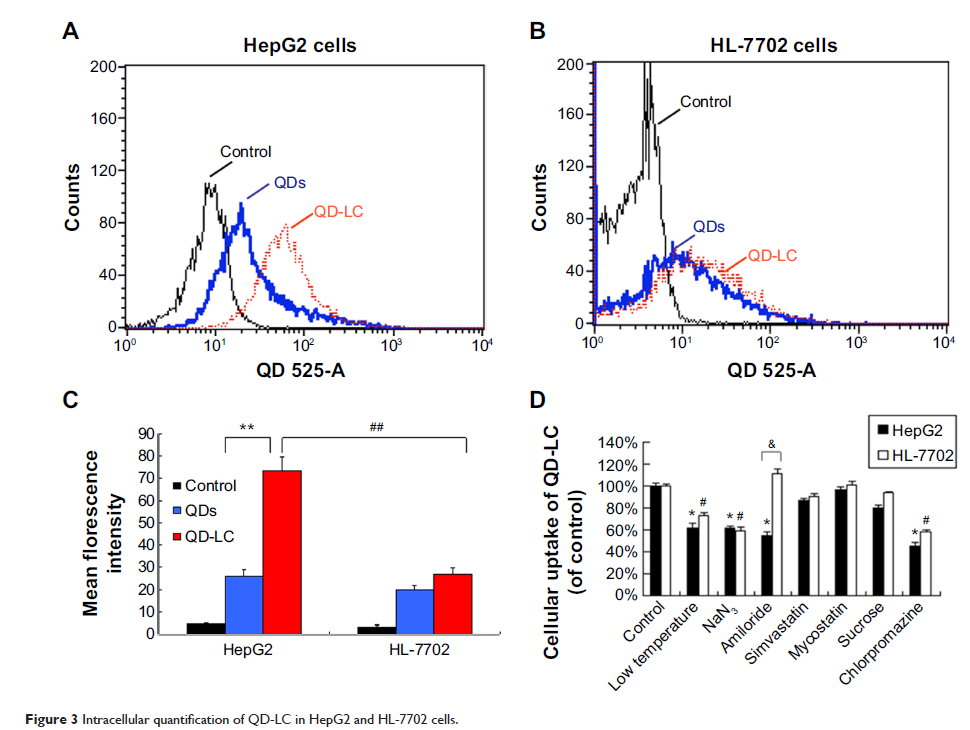
量子点脂质体的因性毒性实现对肝癌发展的选择性抑制
Authors Shao D, Li J, Guan F, Pan Y, Xiao X, Zhang M, Zhang H, Chen L
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 5753—5769
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S73185
Received 25 August 2014, Accepted 4 October 2014, Published 8 December 2014
Abstract: Using the
intrinsic toxicity of nanomaterials for anticancer therapy is an emerging
concept. In this work, we discovered that CdTe/CdS quantum dots, when coated
with lipids (QD-LC) instead of popular liposomes, polymers, or dendrimers,
demonstrated extraordinarily high specificity for cancer cells, which was due
to the difference in the macropinocytosis uptake pathways of QD-LC between the
cancer cells and the normal cells. QD-LC-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis was
concomitant with the activation of the JNK/caspase-3 signaling pathway.
Moreover, QD-LC treatment resulted in a delay in the latent period for
microtumor formation of mouse hepatocarcinoma H22 cells and inhibited tumor
growth, with a reduction of 53.2% in tumor volume without toxicity in major
organs after intratumoral administrations to tumor-bearing mice. Our results
demonstrate that QD-LC could be a very promising theranostic agent against
liver cancer.
Keywords: CdTe/CdS quantum
dot–lipid complex, intrinsic nanotoxicity, selectivity, liver cancer therapy, micropinocytosis