9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

设计和评价利多卡因 (Lidocaine)-丙胺卡因 (prilocaine) 共递送的纳米管药物输送系统,用于局部麻醉止痛治疗: 固体脂质纳米颗粒和纳米结构的脂质载体之间的比较
Authors You P, Yuan R, Chen C
Received 3 May 2017
Accepted for publication 22 August 2017
Published 18 September 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 2743—2752
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S141031
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Junhua Mai
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios Panos
Purpose: Topical anesthesia analgesic therapy has diverse applicability in
solving the barrier properties of skin and unfavorable physicochemical
properties of drugs. Lidocaine (LID) combined with prilocaine (PRI) has been
used as a topical preparation for dermal anesthesia for treatment of conditions
such as paresthesia.
Materials and methods: In this study, for combination anesthesia and
overcoming the drawbacks of LID and PRI, respectively, LID- and PRI-loaded
solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) were
prepared and characterized by determination of their particle size, drug
loading capacity, stability, in vitro drug release behavior and in vitro
cellular viability. Ex vivo skin permeation and in vivo anesthesia analgesic
efficiency of these two systems were also evaluated and compared.
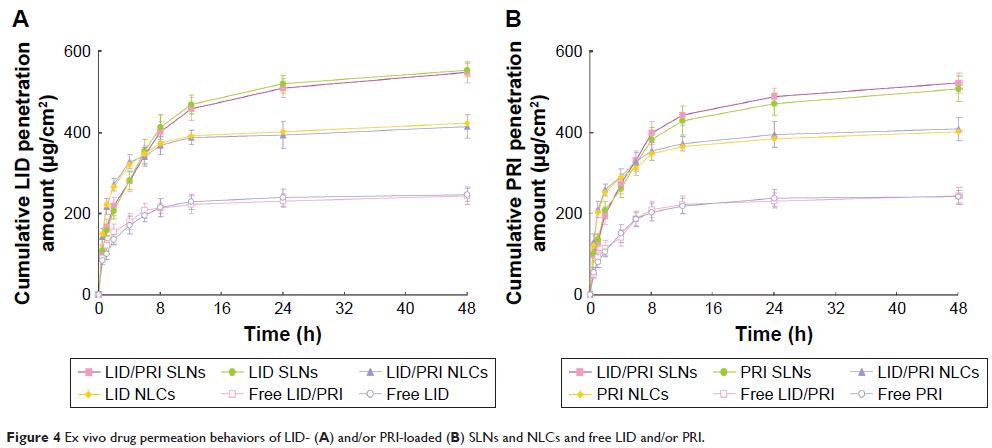
Results: Results revealed that combination delivery of
the dual drugs exhibited more remarkable efficiency than signal drug-loaded
systems. SLN systems have better ex vivo skin permeation ability than NLCs. NLC
systems revealed a stronger in vivo anesthesia analgesic effect than SLN
systems.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that SLNs and NLCs have
different advantages, and that both carriers are promising dual drug delivery
systems for topical anesthetic analgesic therapy.
Keywords: topical
anesthesia, prilocaine, lidocaine, solid lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured
lipid carriers