9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

血管内皮生长因子-A 和基质金属蛋白酶-2 及-9 在子宫内膜癌的血管生成、转移和预后中的作用
Authors Mahecha AM, Wang H
Received 17 January 2017
Accepted for publication 12 July 2017
Published 19 September 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4617—4624
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S132558
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Norbert Ajeawung
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
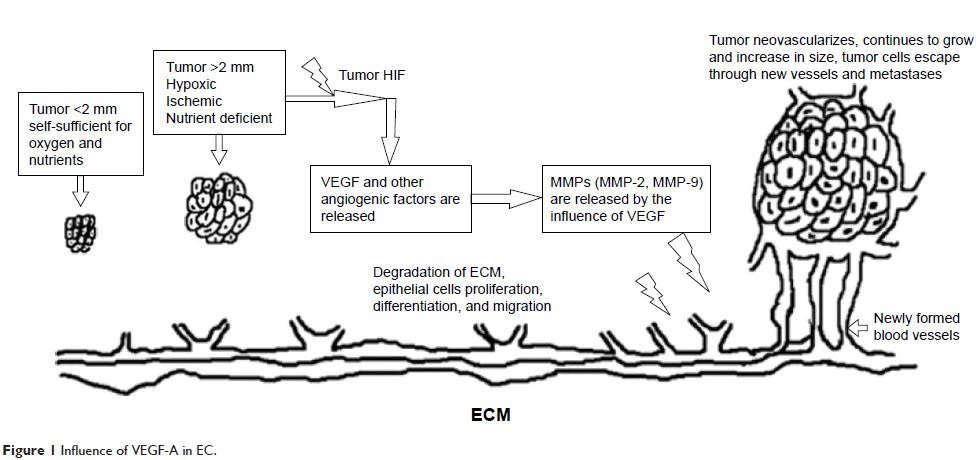
Abstract: Angiogenesis (the
growth of new blood vessels) is essential in most of the body’s physiological
processes, such as in the normal functioning of the endometrium during and
after the menstrual cycle. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix
metalloproteinase (MMP) are the mostly expressed angiogenic factors,
especially, during the process of endometrial degeneration and remodeling. In
carcinogenesis, tumor hypoxia-induced factors, through the process of
“angiogenic switch”, stimulate the production of angiogenic factors,
particularly VEGF and MMP. Subsequently, these angiogenic factors are
associated with degradation, differentiation, proliferation, and migration of
vascular endothelial cells, enhancing the formation of new blood vessels to
supply the tumor with oxygen and nutrients. This process is equally significant
for tumor development and metastasis. Hence, like in other cancers, the
overexpression of MMP and VEGF in endometrial cancer (EC) seems to play a
significant role in its tumorigenesis and metastasis. This research will
discuss the influence of MMP and VEGF on angiogenesis, metastasis, and the
prognosis of EC as well as the clinical importance of the factors in the
diagnosis of EC.
Keywords: angiogenic
switch, angiogenic factors, endometrioid endometrial carcinoma, microvascular
density