9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
白细胞介素-6 上调骨肉瘤中 SOX18 的表达
Authors Wu Z, Yang W, Liu J, Zhang F
Received 24 August 2017
Accepted for publication 2 October 2017
Published 8 November 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5329—5336
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S149905
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Aim: SOX18 is a
potential oncogene in osteosarcoma via controlling osteosarcoma cell
proliferation and metastasis. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a major activator of Janus
kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3)
signaling, plays an important role in the growth of carcinoma cells. The
present study aims to investigate the correlation between IL-6 and SOX18 in
osteosarcoma.
Materials and methods: Protein expression and mRNA expression were determined by Western blot and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis, respectively. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were identified by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay and flow cytometry analysis, respectively.
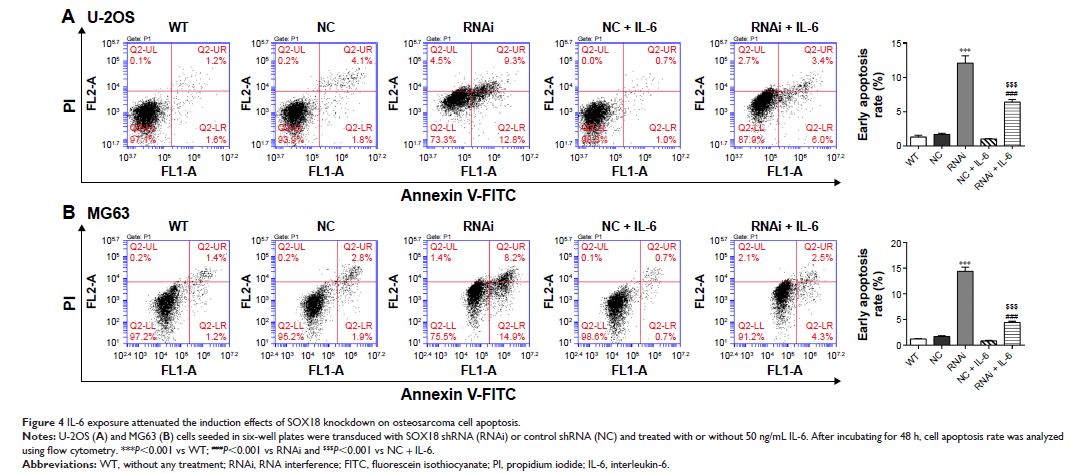
Results: We found that SOX18, IL-6 and p-STAT3 were elevated in osteosarcoma compared with bone cyst tissues. A positive correlation between the mRNA levels of IL-6 and SOX18 was observed in osteosarcoma tissues. IL-6 stimulation dose dependently induced the mRNA and protein levels of SOX18 in U-2OS and MG63 cells. Furthermore, IL-6 significantly rescued the inhibitory and induction effects of SOX18 knockdown on osteosarcoma cell proliferation and apoptosis, respectively. The changes in cell proliferation (PCNA) and apoptosis-related proteins (Bcl-2, Bax and Cleaved-Caspase 3) were in line with the results of cell proliferation and apoptosis assays.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that IL-6 is a possible upstream regulator for SOX18 in osteosarcoma.
Keywords: IL-6, SOX18, osteosarcoma, proliferation, apoptosis
Materials and methods: Protein expression and mRNA expression were determined by Western blot and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis, respectively. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were identified by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay and flow cytometry analysis, respectively.
Results: We found that SOX18, IL-6 and p-STAT3 were elevated in osteosarcoma compared with bone cyst tissues. A positive correlation between the mRNA levels of IL-6 and SOX18 was observed in osteosarcoma tissues. IL-6 stimulation dose dependently induced the mRNA and protein levels of SOX18 in U-2OS and MG63 cells. Furthermore, IL-6 significantly rescued the inhibitory and induction effects of SOX18 knockdown on osteosarcoma cell proliferation and apoptosis, respectively. The changes in cell proliferation (PCNA) and apoptosis-related proteins (Bcl-2, Bax and Cleaved-Caspase 3) were in line with the results of cell proliferation and apoptosis assays.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that IL-6 is a possible upstream regulator for SOX18 in osteosarcoma.
Keywords: IL-6, SOX18, osteosarcoma, proliferation, apoptosis