9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于新一代测序的神经纤维瘤病 1 型患者潜在调节基因的研究
Authors Yang F, Xu S, Liu RW, Shi T, Li XF, Li XB, Chen G, Liu HY, Zhou QH, Chen J
Received 14 November 2017
Accepted for publication 20 December 2017
Published 21 February 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 919—932
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S156998
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
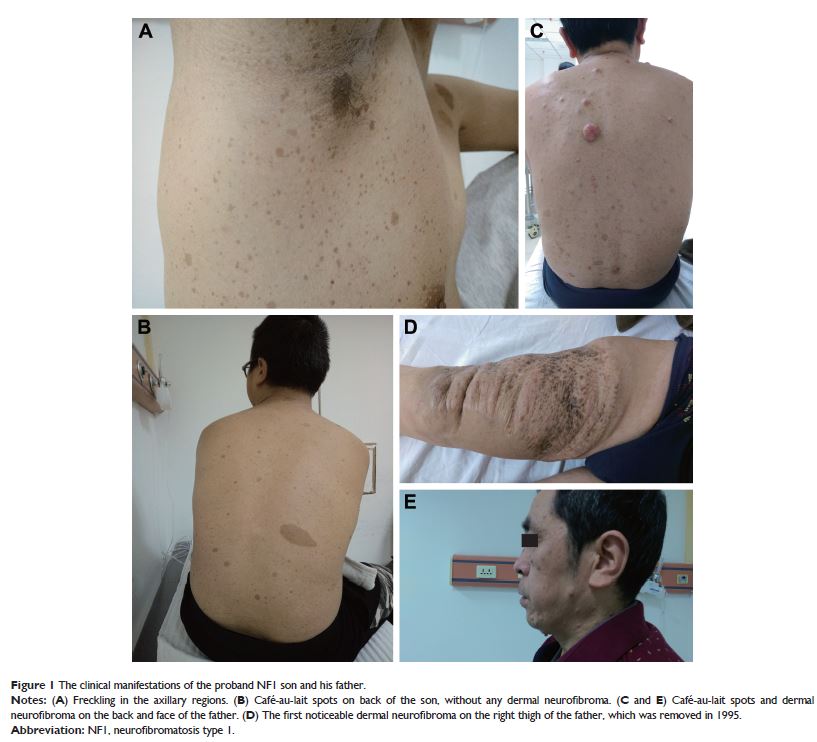
Introduction: Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common Mendelian multi-system
disorder that is characterized by café-au-lait spots (CLS), axillary freckling,
optic glioma and plexiform neurofibroma. Various mutations of the NF1 gene are widely accepted
to be the main cause of this disease, while whether there are still certain
other modifier genes that could influence the phenotypes of NF1 is our concern.
Patients and Methods: One proband and his father are involved, who are
characterized by plexiform neurofibroma and cutaneous neurofibroma,
respectively. Enhanced Computed tomography (CT) and Positron emission
tomography-CT (PET-CT) were taken to collect the radiographic data, and the
specimens of this neurofibroma as well as the blood samples from the father and
son were sent for panel mutation screening of 295 tumor-related genes based on
next-generation screening. Furthermore, the NF1 gene mutations were referred
with Canis lupus familiaris , Rattus norvegicus , Gallus gallus , Danio rerio , and Drosophila melanogaster NF1
sequencing for evolutionary conservativeness and then analyzed in Condel
databases for pathogenicity prediction.
Results: The radiography indicated that the benign
plexiform neurofibroma only occurred in the son. Also, TP53 , FANCA , BCL6 , PIK3C2G , RNF43 , FGFR4 , FLT3 , ERBB2 , PAK7 , NSD1 , MEN1 and TSC1 were uniquely found
mutated in the son, which could be candidates as new modifier genes;
besides, RNF43 was also mutated in public
neurofibroma seuquencing data. By KEGG pathway annotation,
phosphoinositide-3-kinase-Akt pathway was altered in both the public plexiform
neurofibroma sample and in our proband patient.
Conclusion: This study reexamined the background germline
mutations and suggested their potential value as modifier genes that may
influence the phenotype heterogenity.
Keywords: plexiform, neurofibroma
type 1, mutation, modifier gene, next-generation sequencing