9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

低水平的肿瘤抑制剂候选药物 3 预测肝细胞癌患者预后不良
Authors Sheng XR, Xing SG, Wang RD, Chen K, Jia WD
Received 6 October 2017
Accepted for publication 9 January 2018
Published 21 February 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 909—917
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S153381
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Purpose: The tumor suppressor candidate 3 (TUSC3 )
has been considered to be closely associated with the occurrence, development
and invasion of various malignant tumors. However, the expression of TUSC3 in hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) tissues remains ambiguous. The purpose of this research was to
investigate the expression of TUSC3 in HCC
tissues and analyze the relationship between TUSC3 levels
and clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of HCC patients.
Materials and
methods: Immunohistochemistry was used to
detect the expression of TUSC3 in HCC and the corresponding para-cancerous
tissues from 92 samples of HCC patients. mRNA and protein expression levels
of TUSC3 were evaluated by
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot
assays in 25 paired HCC and corresponding adjacent nontumor tissues.
Furthermore, statistical analysis was applied to evaluate the correlation
between TUSC3 level and the clinicopathological features and prognosis of HCC patients.
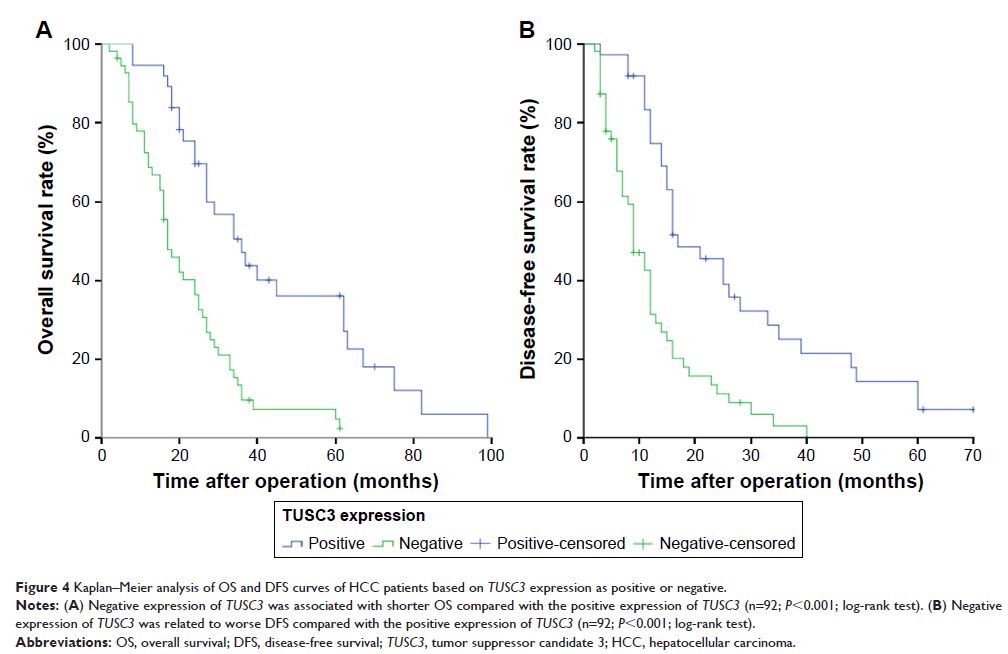
Results: Immunohistochemical assay indicated that the expression of TUSC3 was significantly lower
in HCC tissues when compared with the corresponding para-cancerous tissues (χ 2=11.512, P =0.001). The
analysis of clinicopathological characteristics showed that low expression
of TUSC3 in HCC tissues was
significantly associated with Edmondson grade, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer
stage and tumor size (P =0.008, 0.009 and
0.020, respectively). Univariate analysis showed that the expression of TUSC3 was strongly correlated
with overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) after radical
surgery in HCC patients (P <0.001, P <0.001, respectively).
Multivariate analysis revealed that the TUSC3 level
was an independent risk factor for OS and DFS in HCC patients (P =0.001, P <0.001, respectively). Results
of qRT-PCR and Western blot assays indicated that the level of TUSC3 in HCC tissues was
significantly lower than that in the corresponding adjacent noncancerous
tissues (P <0.01, P <0.001).
Conclusion: The expression of TUSC3 in HCC
was significantly downregulated and was correlated with tumor progression and
prognosis, which could be used as an independent predictor of prognosis in HCC
patients.
Keywords: TUSC3 , hepatocellular carcinoma,
prognosis, immunohistochemistry, overall survival