9 0 4 9 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

伴有中等危险因素的 IB/IIA 期宫颈癌在根治性手术治疗后分别接受顺铂同步放化疗与辅助放疗的效果比较:一项回顾性研究
Authors Sun H, Tang Q, Chen J, Lv X, Tu Y, Yan D
Received 27 November 2017
Accepted for publication 16 January 2018
Published 6 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1149—1155
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S158214
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Purpose: To determine if postoperative cisplatin concurrent
chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) improves the outcome in stage IA/IIB cervical cancer
patients with intermediate risk factors, when compared with radiation therapy
(RT) alone, and identify the potential eligible populations for this treatment.
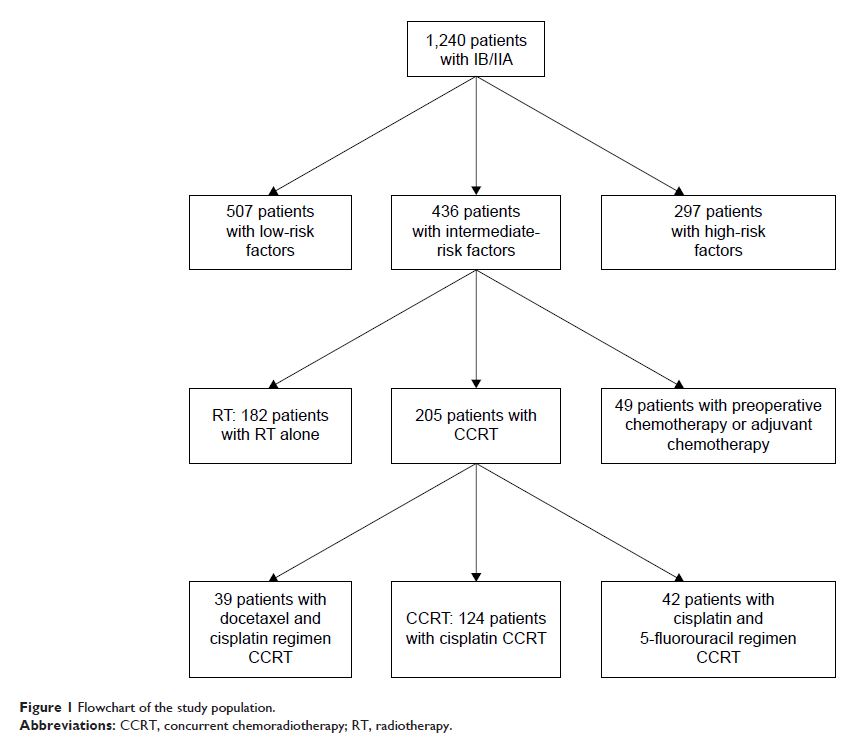
Patients and
methods: We reviewed medical records of 1,240
patients with stage IA/IIB cervical cancer who underwent radical hysterectomy
and pelvic lymphadenectomy in our hospital between January 2008 and December
2011. Of the 1,240 patients, 436 displayed 1 or more intermediate risk factors.
Of these, we screened 306 patients who underwent RT only or CCRT. We analyzed
the effects of CCRT on survival and prognosis.
Results: The 5-year progress-free survival (PFS) in the CCRT group was
superior to that in the RT-only group (96.0% vs 89.0%, respectively; P =0.031). The 5-year overall
survivals (OSs) were not different between the 2 groups (P =0.141). Compared with RT-only
group, CCRT did not improve PFS or OS in patients with 1 risk factor, large
tumor size, or deep stromal invasion (P>0.05).
Compared with RT-only group, CCRT improved PFS (97.9% vs 82.8%; P =0.017) but did not increase OS
(97.9% vs 89.7%; P =0.109) in
patients with lymphovascular space invasion plus deep stromal invasion/large
tumor size. OS (92.3% vs 70.6%; P =0.048) and PFS
(92.3% vs 64.7%; P =0.020) in the
CCRT group were superior to those in the RT-only group with 3 risk factors.
Compared with RT-only group, CCRT was an independent prognostic factor for
favorable PFS (hazard ratio [HR] =0.238; 95% CI =0.0827–0.697, P =0.009) and OS (HR =0.192; 95% CI
=0.069–0.533, P =0.002).
Conclusion: Postoperative CCRT improved survival in stage IA/IIB cervical
cancer patients with intermediate risk factors. Patients with 2 or more
intermediate risk factors, including lymphovascular space invasion, may benefit
from CCRT.
Keywords: cervical cancer, concurrent chemoradiotherapy, intermediate risk
factors