9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

与微血管密度相关的 c-kit 过表达(CD117)是 HBV 相关肝细胞癌患者生存预后的独立因素
Authors Yan W, Zhu Z, Pan F, Huang A, Dai G
Received 20 November 2017
Accepted for publication 7 February 2018
Published 7 March 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 1285—1292
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S157545
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background: To
explore new biomarkers for indicating the recurrence and prognosis in hepatitis
B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients after tumor
resection, we investigated the expression and prognostic value of c-kit(CD117)
in HBV-related HCC.
Materials and
methods: Immunohistochemistry was used to
estimate the expression of c-kit(CD117) and CD34 in the liver cancer tissues.
The correlations between the expression of these biomarkers and the
clinicopathologic characteristics were analyzed.
Results: The positive rate of c-kit(CD117) expression in 206 HCC cases was
48.1%, and c-kit expression was significantly related with CD34-positive
microvessel density. CD34-microvessel density numbers were much higher in
c-kit(+) HCC tissues than in c-kit(-) HCC tissues (44.13±17.01 vs
26.87±13.16, P =0.003). The expression of c-kit
was significantly higher in patients with Edmondson grade III–IV (P <0.001) and TNM stage III (P <0.001). Moreover,
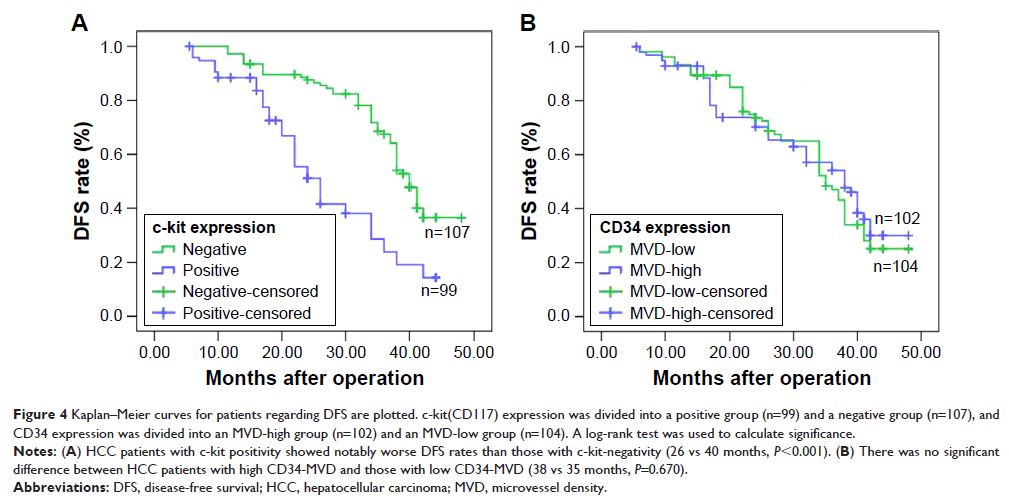
Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that c-kit (P <0.001)
expression was correlated with reduced disease-free survival (DFS).
Multivariate analysis identified c-kit as an independent poor prognostic factor
of DFS in HCC patients (P <0.001).
Conclusion: Increased c-kit expression could be considered as an independent
unfavorable prognostic factor for predicting DFS in HBV-related HCC patients
after surgery. These results could be used to identify patients at a higher
risk of early tumor recurrence and poor prognosis.
Keywords: c-kit, CD34, hepatocellular carcinoma, prognosis, immunohistochemistry