9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

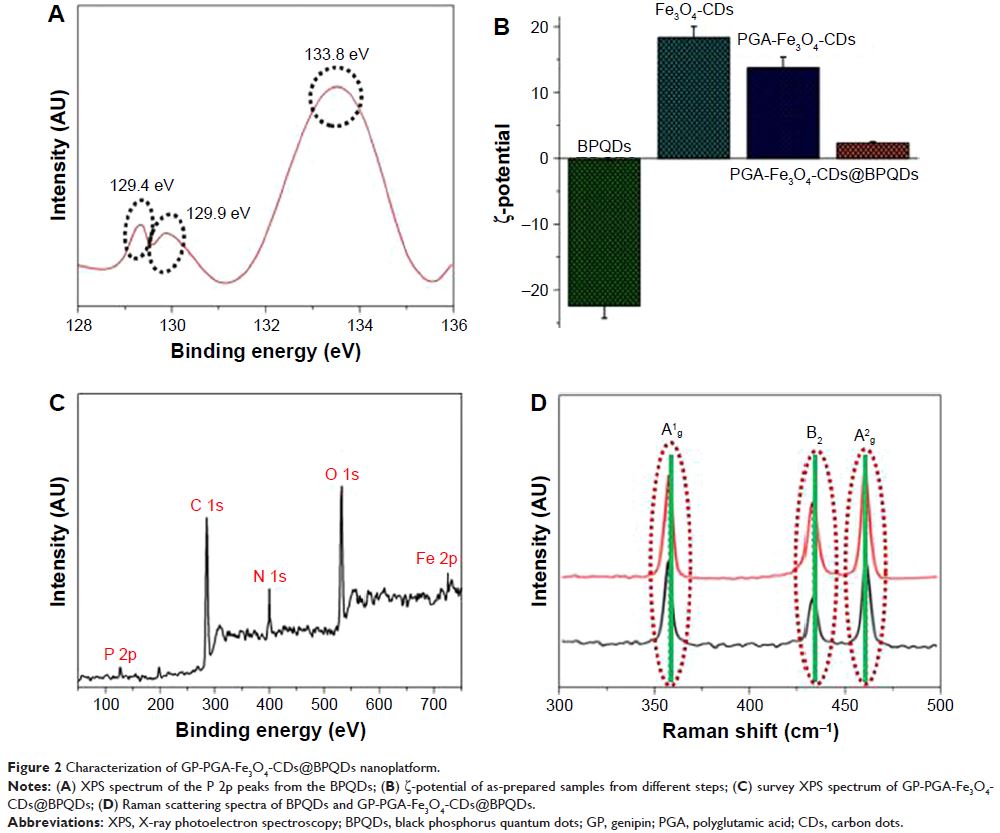
由 Fe3O4 碳点与石墨黑磷量子点组装的近红外光介导的光动力/光热疗法纳米平台
Authors Zhang M, Wang W, Cui Y, Zhou N, Shen J
Received 8 November 2017
Accepted for publication 15 February 2018
Published 10 May 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2803—2819
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S156434
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Recently, combined photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy
(PTT) has become a desired treatment for cancer. However, the development of
economic, high-efficiency, and safe photosensitizers/photothermal agents
remains a significant challenge.
Methods: A novel nanocomposite has been developed via the assembly of iron
oxide carbon dot (Fe3O4-CDs) nanoparticles and
black phosphorus quantum dots (genipin [GP]-polyglutamic acid [PGA]-Fe3O4-CDs@BPQDs), and this
nanocomposite shows a broad light-absorption band and a photodegradable
character.
Results: In vitro and in vivo assays indicated that GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CDs@BPQDs were highly
biocompatible and exhibited excellent tumor-inhibition efficacy, due to the
synergistic PTT and PDT via a near-infrared laser. Importantly, in vivo tumor
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) results illustrated that GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CDs@BPQDs can be
specifically applied for enhanced T 2 MRI of tumors. This work presents the first combined application
of a PDT and PTT effect deriving from BPQDs and MRI from Fe3O4-CDs, which may promote
utilization of black BPQDs in biomedicine.
Conclusion: As expected, GP-PGA-Fe3O4-CDs@BPQDs displayed a
dramatically enhanced ability to destroy tumor cells, due to the synergistic
combination of PTT and PDT.
Keywords: black phosphorus quantum dots, biocompatible, photothermal, photodynamic, T 2 MRI