9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

甘油三萜通过调节大鼠转化生长因子-β1/Smad、核因子-κB 和 AKT 信号通路来改善肝纤维化
Authors Cao S, Zheng B, Chen T, Chang X, Yin B, Huang ZH, Shuai P, Han L
Received 24 October 2017
Accepted for publication 12 March 2018
Published 11 May 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 1205—1213
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S155053
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Palas Chanda
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Purpose: There is no effective treatment for liver fibrosis, which is a
common phase during the progression of many chronic liver diseases to
cirrhosis. Previous studies found that Semen Brassicae therapy can effectively
improve the clinical symptoms of patients with asthma, allergic rhinitis, and
chronic lung diseases; however, its effects on liver fibrosis in rats and its
possible mechanisms of action remain unclear.
Methods: Rats were injected intraperitoneally with 4% thioacetamide aqueous
solution (5 mL·kg-1) at a dose of 200 mg·kg-1 twice a week for 8 consecutive weeks to establish the liver
fibrosis model and were then treated with different concentrations of Semen
Brassicae extract. After Semen Brassicae treatment, the morphology of the liver
tissue was analyzed using hematoxylin and eosin and Masson’s trichrome
staining, and liver index and liver fibrosis grade were calculated. Thereafter,
the levels of collagen-I, collagen-III, α-SMA, transforming growth factor
(TGF)-β1, p-Smad 2/3, Smad 2/3, Smad4, NF-κB-p65, p-NF-κB-p65, IL-1β, IL-6,
AKT, and p-AKT were determined using Western blotting.
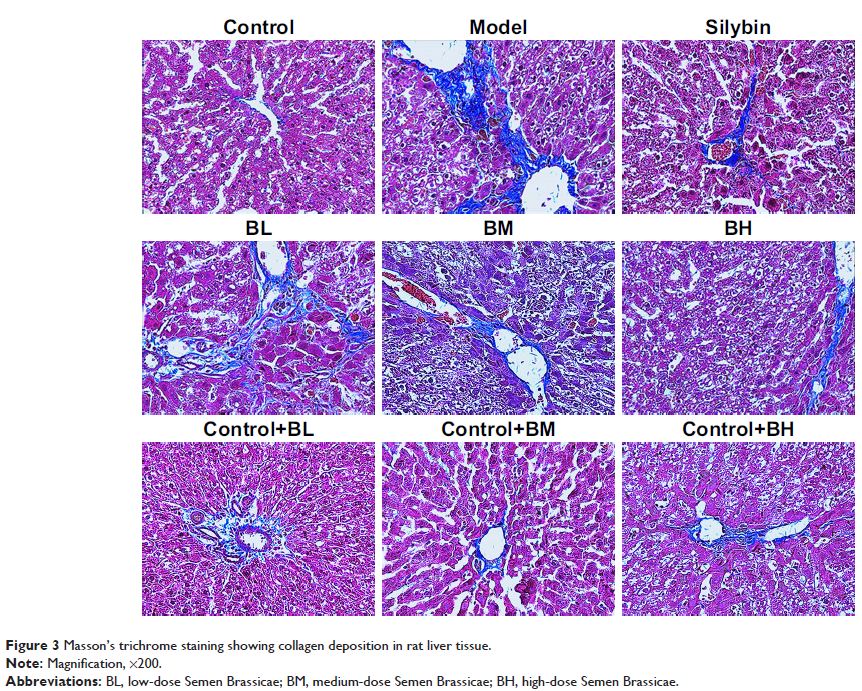
Results: Compared with the untreated model group, the Semen
Brassicae-treated group showed significantly decreased liver function indices;
expression levels of collagen-I, collagen-III, and α-SMA; and hepatic fibrosis.
Further studies also showed that the expression of TGF-β1, Smad4, p-Smad
2/3/Smad 2/3, p-NF-κB-p65/NF-κB-p65, IL-1β, IL-6, and p-AKT/AKT significantly
decreased after the treatment.
Conclusion: These results indicate that Semen Brassicae exhibits an
anti-hepatic fibrosis effect, and the underlying mechanism of action may be
related to the regulation of TGF-β1/Smad, NF-κB, and AKT signaling pathways and
the reduction of extracellular matrix deposition.
Keywords: hepatic fibrosis, Semen Brassicae, NF-κB, AKT, TGF-β1