9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
微核糖核酸 29b 抑制细胞增殖和侵袭,同时以前列腺癌中的 DNMT3b 蛋白和 AKT3 蛋白为靶向,加强顺铂在细胞凋亡和化疗中的作用
Authors Yan B, Guo Q, Nan XX, Wang Z, Yin Z, Yi L, Wei YB, Gao YL, Zhou KQ, Yang JR
Published Date March 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 557—565
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S76484
Received 27 October 2014, Accepted 20 January 2015, Published 4 March 2015
Background: Micro-ribonucleic acids (miRNAs) are crucial regulators in malignant
tumors. miRNA-29b (miR-29b) has been identified as a tumor suppressor in
prostate cancer (PCa). However, very few studies have investigated the effects
of miR-29b in PCa, especially the mechanism and its association with
chemotherapy. Our study aimed to explore the role and mechanism of miR-29b in
PCa.
Materials and methods: The expression levels of miR-29b were detected in ten clinical PCa specimens and four different PCa cell lines through quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. After miR-29b mimics and inhibitors were successfully transfected into LNCaP, the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay was then used to investigate cell proliferation and cisplatin sensitivity of PCa cells. Cell cycle, cell apoptosis, and cell invasion were detected via flow cytometry, annexin V–fluorescein isothiocyanate labeling, and transwell assay, respectively. Based on bioinformatic methods, Western blot analysis, and dual-luciferase reporter assay, novel target genes of miR-29b were identified.
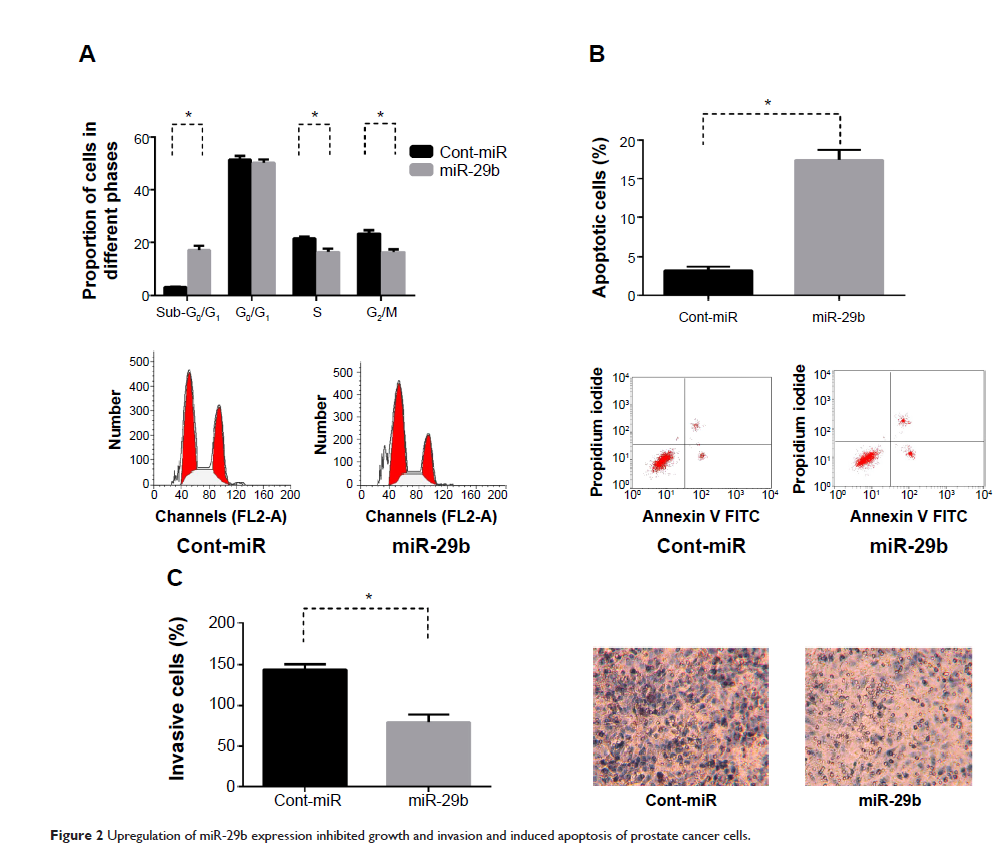
Results: miR-29b was downregulated in PCa tissues compared with matched adjacent nontumor tissues. In the androgen-independent PCa cell line (LNCaP-AI), the expression of miR-29b was much lower than the androgen-dependent PCa cell line (LNCaP). Subsequent studies showed that forced expression of miR-29b inhibited cell proliferation and cell invasion and induced cell apoptosis in PCa. Upregulation of miR-29b also enhanced the chemosensitivity of PCa cells to cisplatin. Moreover, we identified DNMT3b and AKT3 as novel target genes of miR-29b in PCa.
Conclusion: Taken together, the results showed that miR-29b plays a tumor-suppressive role in PCa. It inhibits cell biological behavior and enhances the chemotherapy effects of cisplatin through its involvement in epigenetic regulation and PI3K/AKT pathway.
Keywords: miRNA-29b, prostate cancer, cell biological behavior, chemosensitivity, DNMT3b, AKT3
Materials and methods: The expression levels of miR-29b were detected in ten clinical PCa specimens and four different PCa cell lines through quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. After miR-29b mimics and inhibitors were successfully transfected into LNCaP, the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay was then used to investigate cell proliferation and cisplatin sensitivity of PCa cells. Cell cycle, cell apoptosis, and cell invasion were detected via flow cytometry, annexin V–fluorescein isothiocyanate labeling, and transwell assay, respectively. Based on bioinformatic methods, Western blot analysis, and dual-luciferase reporter assay, novel target genes of miR-29b were identified.
Results: miR-29b was downregulated in PCa tissues compared with matched adjacent nontumor tissues. In the androgen-independent PCa cell line (LNCaP-AI), the expression of miR-29b was much lower than the androgen-dependent PCa cell line (LNCaP). Subsequent studies showed that forced expression of miR-29b inhibited cell proliferation and cell invasion and induced cell apoptosis in PCa. Upregulation of miR-29b also enhanced the chemosensitivity of PCa cells to cisplatin. Moreover, we identified DNMT3b and AKT3 as novel target genes of miR-29b in PCa.
Conclusion: Taken together, the results showed that miR-29b plays a tumor-suppressive role in PCa. It inhibits cell biological behavior and enhances the chemotherapy effects of cisplatin through its involvement in epigenetic regulation and PI3K/AKT pathway.
Keywords: miRNA-29b, prostate cancer, cell biological behavior, chemosensitivity, DNMT3b, AKT3