9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

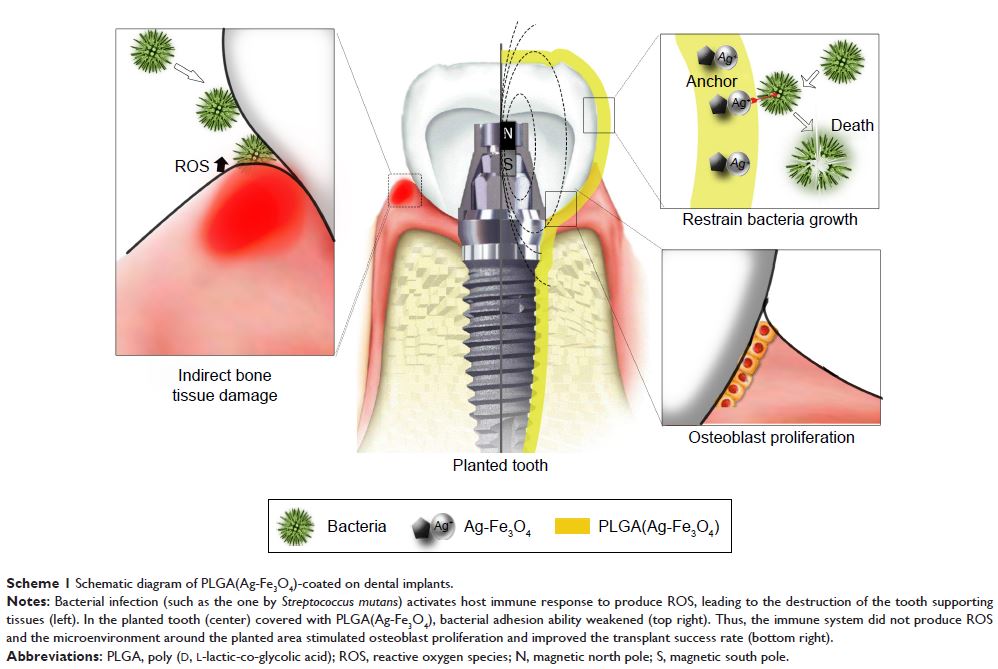
PLGA(Ag-Fe3O4)(四氧化三铁/银复合材料)涂层的牙科植入物在磁场下抑制细菌粘附和成骨诱导的安全性和疗效
Authors Yang Y, Ren S, Zhang X, Yu Y, Liu C, Yang J, Miao L
Received 14 December 2017
Accepted for publication 26 April 2018
Published 28 June 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 3751—3762
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S159860
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Introduction: The placement of dental implants is performed in a contaminated
surgical field in the oral cavity, which may lead to implant failure. Bacterial
adhesion and proliferation (Streptococcus mutans ,
Porphyromonas gingivalis ) often lead to implant infections.
Although Ag nanoparticles hold great promise for a broad spectrum of
antibacterial activities, their runoff from dental implants compromises their
antibacterial efficacy and potentially impairs osteoblast proliferation. Thus,
this aspect remains a primary challenge and should be controlled.
Materials and
methods: In this study, PLGA(Ag-Fe3O4) was modified on the
implanted tooth surface and was characterized by transmission electron
microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The
magnetic and antibacterial properties were also determined.
Results: Results showed that Ag successfully bonded with Fe3O4, and Ag-Fe3O4 not only exerted
superparamagnetism but also exhibited antibacterial activity almost identical
to silver nanoparticles (nano-Ag). The PLGA(Ag-Fe3O4) coating could significantly
maintain the antibacterial activity and avoid bacterial adhesion to the
implant. Compared with the blank control group, PLGA(Ag-Fe3O4) under magnetic
field-coated samples had a significantly lower amount of colonized S. mutans (P <0.01). Osteoblast proliferation
results showed that the coated samples did not exhibit cytotoxicity and could
promote osteoblast proliferation as shown by MTT, alkaline phosphatase, and the
nucleolar organizer region count.
Conclusion: We developed a novel Ag biologically compatible nanoparticle in
this study without compromising the nano-Ag antibacterial activity, which
provided continuous antibacterial action.
Keywords: Ag-Fe3O4, PLGA, dental
implants, antibacterial property