9 0 4 9 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

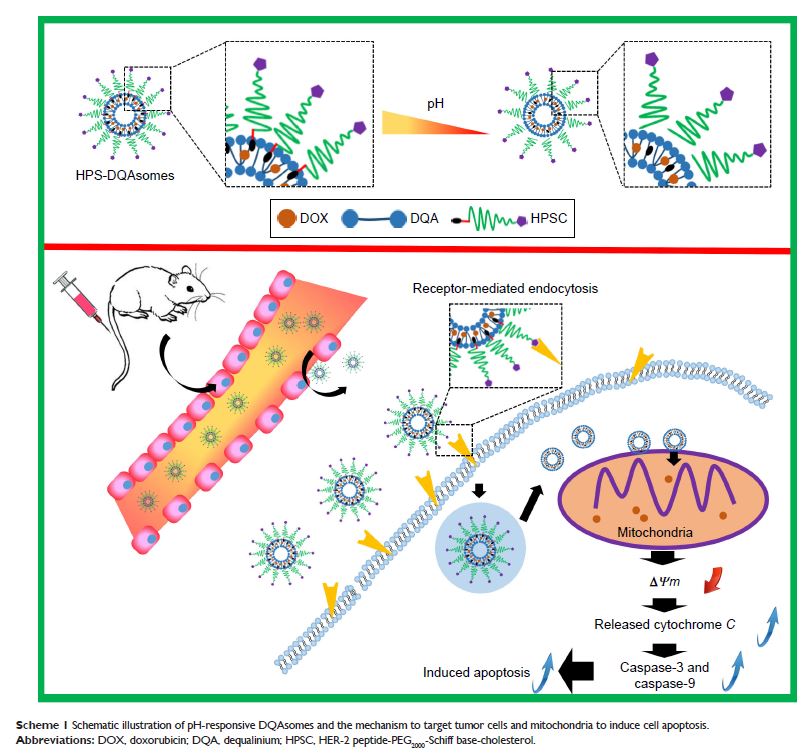
多柔比星的线粒体靶向递送可增强 HER-2 肽介导的多功能、pH 敏感性 DQAsomes 的抗肿瘤活性
Authors Shi M, Zhang J, Li X, Pan S, Li J, Yang C, Hu H, Qiao M, Chen D, Zhao X
Received 26 January 2018
Accepted for publication 24 April 2018
Published 18 July 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 4209—4226
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S163858
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Introduction: Multidrug
resistance (MDR) of breast cancer is the major challenge to successful
chemotherapy while mitochondria-targeting therapy was a promising strategy to
overcome MDR.
Materials and
methods: In this study, HER-2 peptide-PEG2000-Schiff base-cholesterol (HPSC) derivate was synthesized successfully
and incorporated it on the surface of the doxorubicin (DOX)-loaded dequalinium
(DQA) chloride vesicle (HPS-DQAsomes) to treat drug-resistant breast cancer.
Evaluations were performed using human breast cancer cell and DOX-resistant
breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR).
Results: The particle size of HPS-DQAsomes was ~110 nm with spherical
shape. In vitro cytotoxicity assay indicated that HPS-DQAsomes could increase
the cytotoxicity against MCF-7/ADR cell line. Cellular uptake and
mitochondria-targeting assay demonstrated that HPS-DQAsomes could target
delivering therapeutical agent to mitochondria and inducing mitochondria-driven
apoptosis process. In vivo antitumor assay suggested that HPS-DQAsomes could
reach favorable antitumor activity due to both tumor targetability and
sub-organelles’ targetability. Histological assay also indicated that
HPS-DQAsomes showed a strong apoptosis-inducing effect. No obvious systematic
toxicity of HPS-DQAsomes could be observed.
Conclusion: In summary, multifunctional HPS-DQAsomes provide a novel and
versatile approach for overcoming MDR via mitochondrial pathway in cancer
treatment.
Keywords: mitochondrial target, DQAsomes, pH responsive, HER-2 peptide