9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

金纳米粒子与肽共轭的神经细胞的具体成像新策略
Authors Zhang E, Fu A
Published Date March 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 2115—2124
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S78554
Received 2 December 2014, Accepted 25 January 2015, Published 16 March 2015
Abstract: Despite the
significant progress in molecular imaging technologies that has been made in
recent years, the specific detection of neural cells still remains challenging.
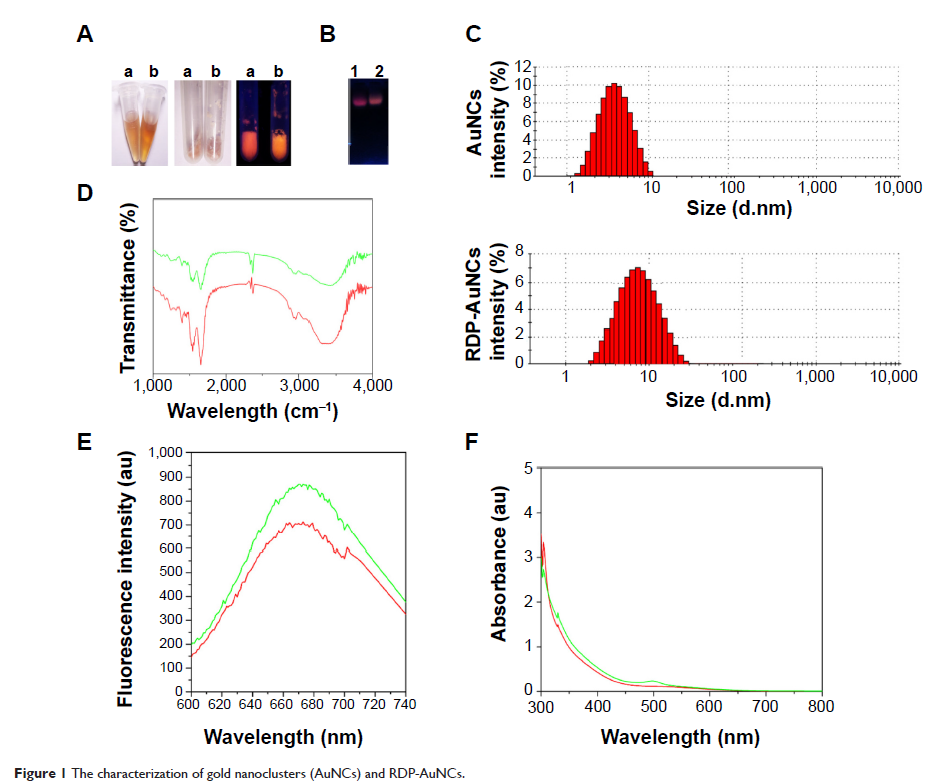
Here, we suggest the use of gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) modified with a
brain-targeting peptide as a potential imaging candidate for detecting neural
cells in vitro and in mice. AuNCs of less than 10 nm (dynamic light scattering
analysis) were first prepared using the “green” synthetic approach, and then a
targeting peptide, rabies virus glycoprotein derived peptide (RDP), was
conjugated to the AuNCs for improving the efficiency and specificity of neural
cell penetration. The conjugate’s mechanism of cellular attachment and entry
into neural cells was suggested to be receptor-mediated endocytosis through
clathrin-coated pits. Also, noninvasive imaging analysis and animal studies
indicated that the RDP-modified nanoclusters could concentrate in the brain and
locate in neural cells. This study suggests the feasibility of using targeting
peptide-modified nanoclusters for noninvasive imaging brain cells in vivo.
Keywords: RDP, targeted
delivery, bioimaging, brain