9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

ALK -重排肺神经内分泌癌:对罕见病例系列和文献综述的综合研究
Authors Zheng Q, Zheng M, Jin Y, Shen X, Shan L, Shen L, Sun Y, Chen H, Li Y
Received 24 April 2018
Accepted for publication 13 June 2018
Published 17 August 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 4991—4998
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S172124
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
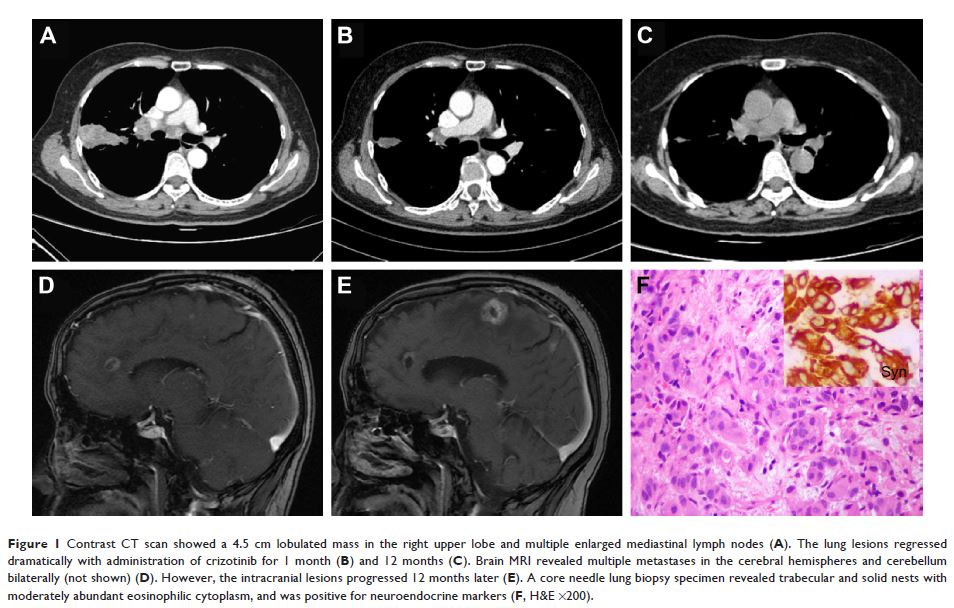
Abstract: Driver mutations involving tyrosine kinase receptors play crucial roles in the oncogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma. However, receptor tyrosine kinase mutations are extremely rare events in primary pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC), which is a molecular heterogeneous entity. In this study, we examined 4 cases of NEC with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK ) rearrangement between 2008 and 2018 at our hospital. We comprehensively analyzed the carcinomas’ clinicopathological features, genetic alterations, and response to ALK inhibitor. One case of atypical carcinoid tumor and 1 case of large cell NEC (LCNEC) achieved response to ALK inhibitor (crizotinib) treatment. One case of combined LCNEC with adenocarcinoma harboring KLC1-ALK (K9:A20) fusion genes was confirmed by NGS of both components, while only the LCNEC component presented RB1 mutation. Notably, tumor cells of different components exhibited different ALK -positive signal patterns by fluorescence in situ hybridization, which revealed isolated 3' signals in the adenocarcinoma component but split signals in the LCNEC. As the largest case series study, our findings suggested that preliminary screening for ALK rearrangement should also be considered in atypical carcinoid and high-grade NEC. Patients with ALK rearrangement-positive NEC would benefit from ALK inhibitor intervention.
Keywords: anaplastic lymphoma kinase, driver mutation, neuroendocrine carcinoma, tumor evolution