9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

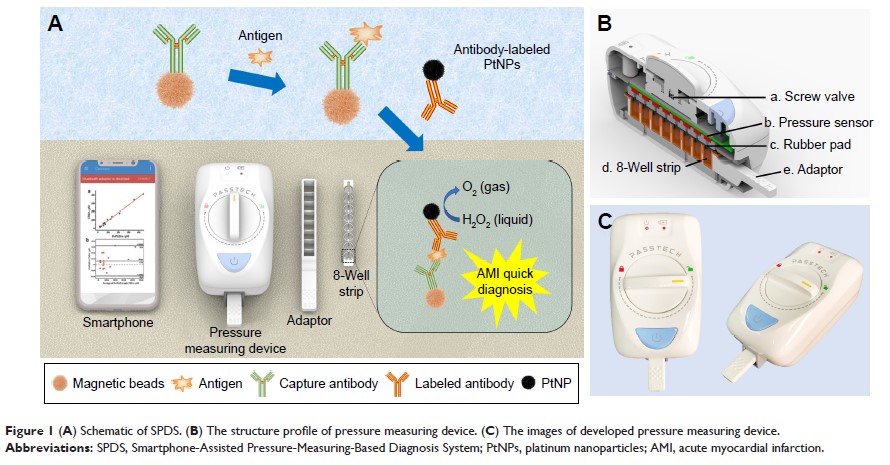
智能手机辅助的、基于压力测量的急性心肌梗死诊断系统
Authors Hong G, Rui G, Zhang D, Lian M, Yang Y, Chen P, Yang H, Guan Z, Chen W, Wang Y
Received 8 December 2018
Accepted for publication 15 February 2019
Published 8 April 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2451—2464
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S197541
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Background: Acute
myocardial infarction (AMI), usually caused by atherosclerosis of coronary
artery, is the most severe manifestation of coronary artery disease which
results in a large amount of death annually. A new diagnosis approach with high
accuracy, reliability and low measuring-time-consuming is essential for AMI
quick diagnosis.
Purpose: The
objective of this study was to develop a new point-of-care testing system with
high accuracy and reliability for AMI quick diagnosis.
Patients and methods: 50 plasma
samples of acute myocardial infarction patients were analyzed by developed
Smartphone-Assisted Pressure-Measuring-Based Diagnosis System (SPDS). The
concentration of substrate was firstly optimized. The effect of antibody
labeling and matrix solution on measuring result were then evaluated. And
standard curves for cTnI, CK-MB and Myo were built for clinical sample
analysis. The measuring results of 50 clinical samples were finally evaluated
by comparing with the measuring result obtained by CLIA.
Results: The
concentration of substrate H2O2 was firstly optimized as 30% to increase
measuring signal. A commercial serum matrix was chosen as the matrix solution
to dilute biomarkers for standard curve building to minimize matrix effect on
the accuracy of clinical plasma sample measuring. The standard curves for cTnI,
CK-MB and Myo were built, with measuring dynamic range of 0–25 ng/mL, 0–33
ng/mL and 0–250 ng/mL, and limit of detection of 0.014 ng/mL, 0.16 ng/mL and
0.85 ng/mL respectively. The measuring results obtained by the developed system
of 50 clinical plasma samples for three biomarkers matched well with the
results obtained by chemiluminescent immunoassay.
Conclusion: Due to
its small device size, high sensitivity and accuracy, SPDS showed a bright
potential for point-of-care testing (POCT) applications.
Keywords: acute
myocardial infarction, diagnosis, pressure sensor, smartphone, Pt nanoparticle