9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

FOXP1 和 FOXO3a 在肝外胆管癌中的表达及其临床病理学意义和预后意义
Authors He J, Yang Z, Wu Z, Wang L, Xu S, Zou Q, Yuan Y, Li D
Received 4 December 2018
Accepted for publication 23 March 2019
Published 17 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2955—2965
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197001
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Gaetano Romano
Aims: Extrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma (EHCC) is a highly malignant tumor with poor prognosis and
intrinsic resistance to cytotoxic agents. The molecular mechanisms associated
with high malignancy and resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy have not
been fully elucidated. This study investigated the clinicopathological
significances of FOXP1 and FOXO3a expression in EHCC.
Methods: We
assayed FOXP1 and FOXO3a expressions in 100 EHCC, 30 peritumoral tissues, 10
adenoma and 15 normal biliary tract tissues using EnVision
immunohistochemistry.
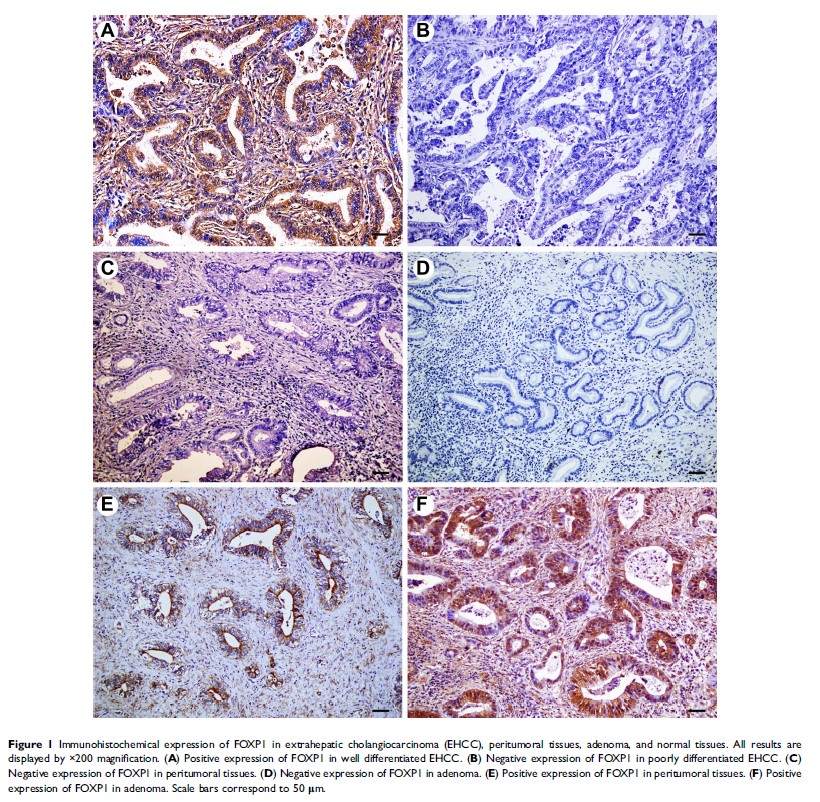
Results: The
positive rates of FOXP1 and FOXO3a proteins were significantly lower in EHCC
tumors than in peritumoral tissues, adenoma, and normal bile tract tissues (P <0.01). Adenoma
and pericancerous tissues with negative FOXP1 and/or FOXO3a protein expressions
exhibited atypical hyperplasia. The positive correlation was established
between the expression of FOXP1 and FOXO3a in EHCC (P <0.01). The
positive rates of FOXP1 and FOXO3a expression were significantly higher in
cases with well differentiation, no metastasis in lymph node, no invasion to
surrounding tissues and organs, TNM I + II stage and radical resection (p <0.05 or p <0.01).
Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that EHCC patients with positive FOXP1
and FOXO3a expression survived significantly higher than patients with negative
FOXP1 and FOXO3a expression, respectively (P <0.001). Cox multivariate analysis revealed that
negative FOXP1 or FOXO3a expressions were independent poor prognostic factors
in EHCC patients. The AUCs for FOXP1 and FOXO3a were 0.676 (95% CI:
0.589–0.763, P <0.001) and
0.652 (95% CI: 0.563–741, P =0.002), respectively.
Conclusion: The
present study indicates that negative FOXP1 and FOXO3a expressions are closely
associated with the pathogenesis, clinical, pathological and biological
behaviors, and poor prognosis in EHCC.
Keywords: extrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma, biliary tract adenoma, FOXP1, FOXO3a, immunohistochemistry