9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

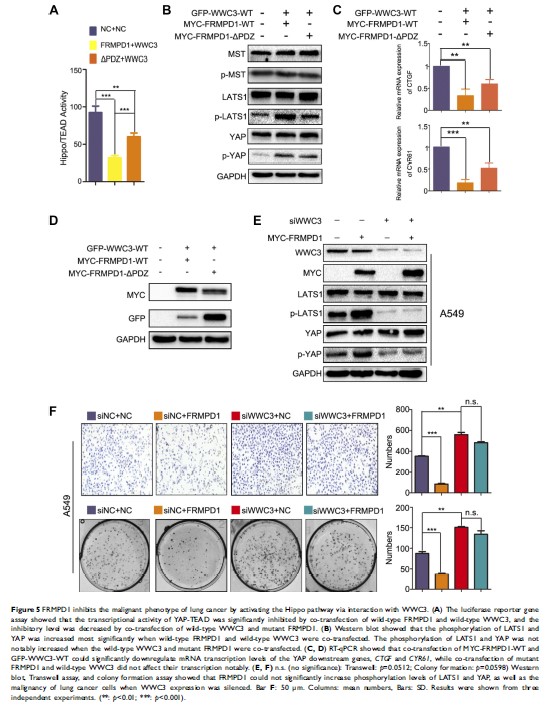
FRMPD1 通过与 WWC3 的相互作用激活 Hippo 通路以抑制肺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭
Authors Rong X, Han Q, Lin X, Kremerskothen J, Wang E
Received 14 November 2018
Accepted for publication 17 March 2019
Published 18 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3395—3410
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S194512
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Purpose: The
expression of FERM-domain-containing protein-1 (FRMPD1)/FERM and PDZ
domain-containing protein-2 (FRMD2) in malignant tumors, including lung cancer,
and its underlying molecular mechanism have not been reported yet.
Materials and methods: Immunohistochemistry
was performed to analyze the expression of FRMPD1 in lung cancer tissues, and
statistical analysis was applied to analyze the relationship between FRMPD1
expression and clinicopathological factors. The biological effects of FRMPD1 on
lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion were determined by functional
experiments both in vivo and in vitro. Immunoblotting, RT-qPCR, dual-luciferase
assay, and immunofluorescence were performed to demonstrate whether FRMPD1 stimulates
Hippo signaling. Co-immunoprecipitation assays were used to clarify the
underlying role of FRMPD1 in Hippo pathway activation via interaction with WW
and C2 domain containing protein-3 (WWC3).
Results: We found
that FRMPD1 expression in lung cancer specimens was lower than that in normal
bronchial epithelium and normal submucosal glands. FRMPD1 expression had a
negative correlation with age, Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) stage, lymph node
metastasis, as well as poor prognosis. Moreover, ectopic expression of FRMPD1
significantly inhibited the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells,
and inhibition of FRMPD1 expression led to opposite effects. Mechanistically,
we found that FRMPD1 interacted with the C-terminal PDZ binding motif of WWC3
via its PSD95/DLG/ZO1 (PDZ) domain and promoted the phosphorylation of large
tumor suppressor-1 (LATS1), thus inhibiting the nuclear translocation of
yes-associated protein (YAP).
Conclusion: FRMPD1
could activate the Hippo pathway and ultimately inhibit the malignant behavior
of lung cancer cells through its interaction with WWC3. This work will provide
an important experimental basis for the discovery of novel biomarkers of lung
cancer and the development of targeted drugs.
Keywords: FRMPD1,
Hippo pathway, LATS1, NSCLC, WWC3