9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

NRF3 抑制乳腺癌细胞转移和细胞增殖,并且是乳腺癌存活的有利预测因子
Authors Sun J, Zheng Z, Chen Q, Pan Y, Lu H, Zhang H, Yu Y, Dai Y
Received 7 December 2018
Accepted for publication 15 March 2019
Published 18 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3019—3030
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197409
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Cancer
metastasis is the leading cause of cancer-related death in breast cancer.
However, our understanding of its mechanisms is still limited. At this study,
the biological roles and clinical significance of NRF3 (NFE2L3, nuclear factor,
Erythroid 2 Like 3) in breast cancer are evaluated for the first time.
Methods: NRF3
expression in breast cancer cell lines and clinical specimens was determined by
western blot and immunohistochemistry, respectively. Cell proliferation, cell
cycle distribution, cell migration, and invasion were detected by MTT, colony
formation, flow cytometry, and transwell assays, respectively. All other
proteins were measured by western blot. The clinical significance of NRF3 was
analyzed using the data from tissue microarray.
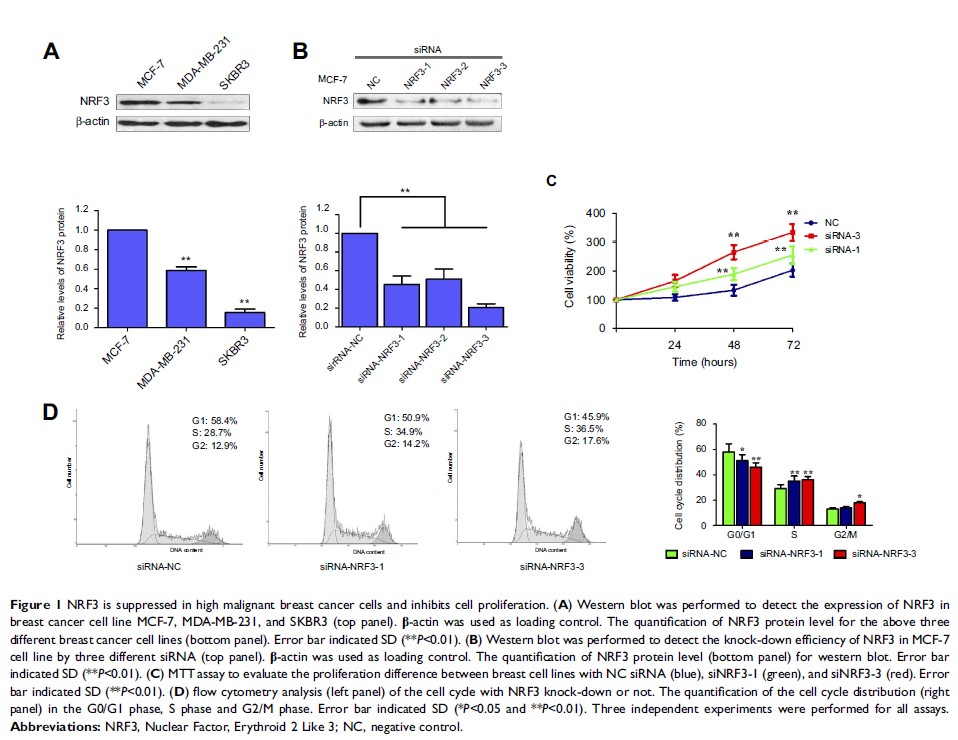
Results: We found
that NRF3 expression was obviously suppressed in breast cancer tissues, and
negatively associated with the Lymph node metastasis status and tumor stages.
Our data also indicated NRF3 expression was much higher in MCF-7 cells than
that in MDA-MB-231 and SKBR3 cells which were more malignant. Silence of NRF3
in MCF-7 cells could significantly promote cell proliferation by reducing the
cell number in the G0/G1 phase. Exogenous expression of NRF3 in SKBR3 and
MDA-MB-231 cells effectively inhibited both cell growth and metastasis with
epithelial–mesenchymal transition and MMPs expression suppressed. NRF3
overexpression also impaired the ID3 expression by inactivating the AKT
signaling pathway. Exogenous expression of ID3 could not only effectively
promote breast cancer cell invasion by inhibiting E-cadherin expression and
upregulating MMP-2 expression, but also attenuated the inhibitory function of
NRF3 on the breast cancer cell invasion.
Conclusion: Our
findings suggested that NRF3 inhibited breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis
via inhibiting AKT/ID3 axis at least partially, and potentially to be a
valuable clinic marker in breast cancer prognosis.
Keywords: human
breast cancer, NRF3, metastasis, EMT, AKT/ID3, overall survival