9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

CD40L 通过抑制 PI3K/Akt 通路抑制 THP-1 细胞的细胞生长
Authors Feng Z, Chen Q, Ren M, Tian Z, Gong Y
Received 25 May 2018
Accepted for publication 13 January 2019
Published 18 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3011—3017
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S175347
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Introduction: Acute
myeloid leukemia (AML), the hematological malignant tumor with high mortality,
is still difficult to treat. CD40L is a type II transmembrane protein, which
has been reported to have the potential to inhibit growth of some cancer cells.
Materials and methods: In order
to determine the role of CD40L on AML-M5 cell line THP-1, we overexpressed
CD40L in the cells using a lentiviral vector system (pHBLV-CMVIE-Zs
Green-T2A-puro vector); overexpression was confirmed by the detection of green
fluorescent protein and CD40L protein expression.
Results: Cellular
apoptosis, proliferation, and cycle assays showed that CD40L could promote the
apoptosis of, suppress the proliferation of, and stimulate the arrest of the
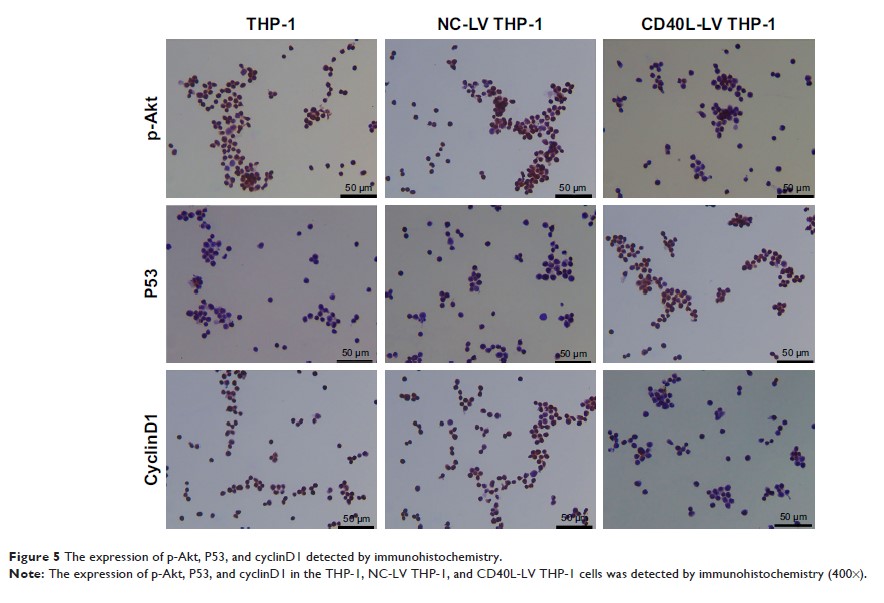
G1/S phase of THP-1 cells. Finally, the protein expression of P53, Bax/Bcl-2,
cyclinD1, PCNA, PTEN, and p-Akt illustrated that CD40L may partly influence
cell growth of THP-1 cells through those genes, which was confirmed by
immunohistochemistry and a PI3K/Akt activator.
Conclusion: Taken
together, CD40L could inhibit cell growth of THP-1 cells through the PI3K/Akt
pathway, indicating that the overexpression of CD40L may be a potential target
to treat the AML-M5 disease.
Keywords: CD40L,
cell proliferation, AML-M5, P53, cyclinD1, PCNA, tumor suppressor, cell
apoptosis