9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

NEDD9 过度表达预示实体癌的预后不良:荟萃分析
Authors Gu Y, Lu J, Chen C, Zheng F
Received 17 February 2019
Accepted for publication 26 April 2019
Published 28 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 4213—4222
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S205760
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background: The
oncogenicity of neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally
down-regulated 9 (NEDD9) has been demonstrated in multiple cancer types.
However, the prognostic value of NEDD9 in some solid cancers remains
controversial. Thus, this meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the
relationship between NEDD9 expression survival rates in solid tumors.
Method: Our
meta-analysis included studies searched from various search engines with
specific inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria. Combined HRs for overall
survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) or progression-free survival
(PFS) or recurrence-free survival (RFS) or cancer-specific survival (CSS) were
assessed using fixed-effects and random-effects models. The source of heterogeneity
was identified by subgroup analysis. Additionally, publication bias was
assessed using funnel plot and Egger’s regression asymmetry test.
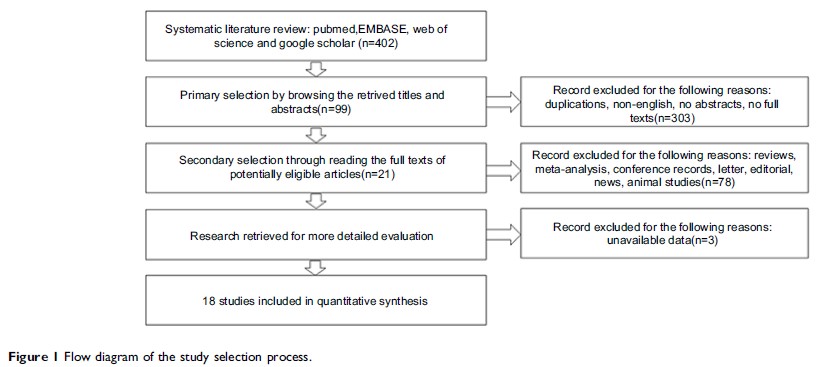
Result: Eighteen
studies with a total of 2,476 patients were retrieved for analysis. Pooled HRs
and 95% CIs were calculated. Both OS (HR=1.82; 95% CI: 1.43–2.31) and
DFS/PFS/RFS/CSS (HR=2.54; 95% CI: 1.93–3.33) indicated that NEDD9
overexpression is associated with poor OS in cancer patients with solid tumors.
Conclusion: NEDD9
overexpression might be a potential marker to predict prognosis in solid cancer
patients.
Keywords: NEDD9,
solid cancer, prognosis, meta-analysis