9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

从猪中回收的作为 mcr-1 及 bla CTX-M-15 共同宿主的多药耐药性大肠杆菌的高发病率
Authors Shafiq M, Huang J, Ur Rahman S, Shah JM, Chen L, Gao Y, Wang M, Wang L
Received 21 March 2019
Accepted for publication 18 June 2019
Published 16 July 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2135—2149
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S209473
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Purpose: The coexistence of mobile colistin (COL)-resistant gene mcr-1 with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) gene in Escherichia coli has become a serious threat globally. The aim of this study was to investigate the increasing resistance to COL and in particular its coexistence with ESBL-producing E. coli recovered from pig farms in China.
Materials and methods: E. coli were isolated from 14 pig farms in Jiangsu China. Susceptibility testing was identified by micro-dilution method. PCR assay and nucleotide sequencing were used to detect COL-resistant genes, mcr -1 to −5, as well as ESBL genes, bla CTX-M, bla SHV and bla TEM. Conjugation experiment, plasmid replicon typing of the multidrug resistance (MDR), S1-PFGE and DNA southern hybridization were performed to study the transferability of these genes.
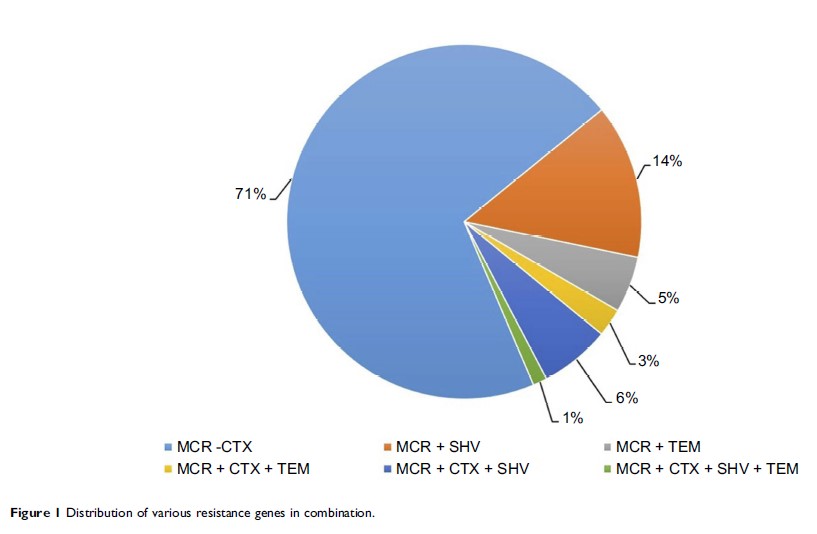
Results: Overall, 275 E. coli isolates were recovered from a total of 432 cloacal and nasal swabs. More than 90% of the isolates were MDR, of which 70.18% were resistant to COL. Of these 275 isolates, mcr-1 was identified as the most predominant gene carried by 71.63% (197/275) of isolates, 39.59% (78/197) of the isolates were harboring both mcr-1 and ESBL genes (bla CTX-M, bla SHV and bla TEM). ESBL genotyping showed that bla CTX-M was the most predominant ESBL (68.49%) followed by bla SHV (16.4%) and bla TEM (15%). Sequencing revealed that the most common variants of bla CTX-M identified were, bla CTX-M-15 (69%), bla CTX-M-55 (29%) and bla CTX-M-1 (1.8%). IncHI2, IncFIB, IncFIC, IncN and IncX4 were found to be the most common Inc-types found both in donors and in transconjugants and were associated with the transfer of the mcr-1 and ESBL encoding genes. Six strains carried a total of five different plasmids: approximately 97-, 130-, 160-, 227- and 242-kb plasmids.
Conclusion: The coexistence of the mcr-1- and bla CTX-M-15-carrying isolates displaying high MDR, recovered from E. coli of pig origin, is a major concern for both humans and veterinary medicine.
Keywords: E. coli , colistin, mcr-1 , ESBL, coexistence