9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

辛伐他汀预处理可改善 t-PA 诱导的血栓栓塞性脑缺血大鼠出血转化和 MMP-9/TIMP-1 失衡
Authors Yin B, Li DD, Xu SY, Huang H, Lin J, Sheng HS, Fang JH, Song JN, Zhang M
Received 29 December 2018
Accepted for publication 1 May 2019
Published 16 July 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 1993—2002
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S199371
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jun Chen
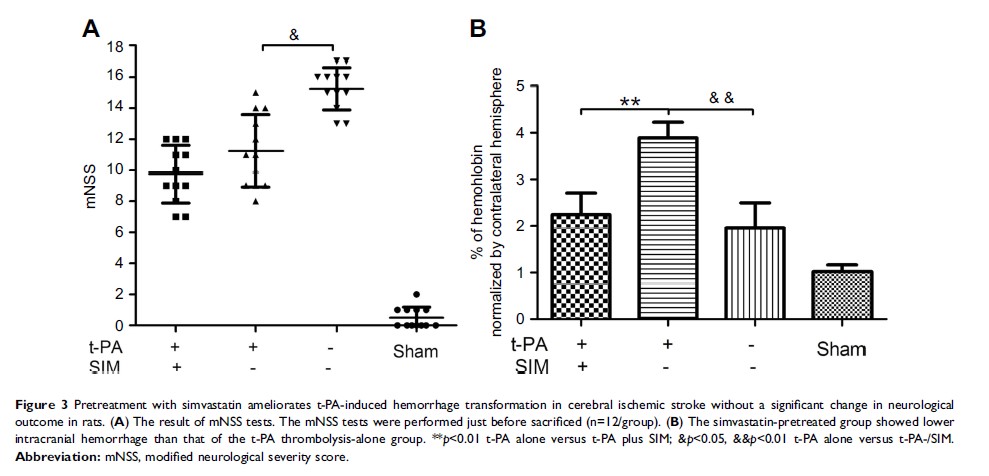
Background: The use of thrombolysis with tissue-plasminogen activator (t-PA) in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is limited by increased levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and by the increased risk of hemorrhagic transformation (HT). In this study, we investigated the effects of simvastatin pretreatment on t-PA-induced MMP-9/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) imbalance and HT aggravation in a rat AIS model.
Methods: The rat AIS model was established by autologous blood emboli. Two weeks before surgery, rats were pretreated with simvastatin (60 mg/kg/d), and three hours after surgery, t-PA (10 mg/kg) was administered. MMP-9 and TIMP-1 levels in the infarcted zone and plasma were evaluated by Western blot analysis and ELISA; the level of HT was quantified by determining the hemoglobin content. RhoA activation was determined to clarify the potential effect.
Results: The results suggested that pretreatment with simvastatin suppressed the increase in t-PA-induced MMP-9 levels and neutralized the elevated MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio, but had no effect on TIMP-1 levels. Thrombolysis with t-PA after ischemia improved neurological outcome, but increased intracranial hemorrhage. Moreover, t-PA-induced HT aggravation was reduced by simvastatin pretreatment. In addition, we showed that t-PA-induced activation of RhoA was suppressed by simvastatin, and that t-PA-induced MMP-9/TIMP-1 imbalance and hemorrhage was reduced by Rho kinases (ROCK) inhibitor Y-27632.
Conclusion: In this study, we showed that simvastatin pretreatment ameliorated t-PA-induced HT and MMP-9/TIMP-1 imbalance, and demonstrated that the RhoA/ROCK pathway was implicated.
Keywords: simvastatin, acute ischemic stroke, t-PA, MMP-9/TIMP-1, RhoA/ROCK pathway, hemorrhagic transformation