9 0 6 7 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

小鼠 Mn 掺杂 ZnS 量子点的毒性和血清代谢组学研究
Authors Yang Y, Lv S, Wang F, An Y, Fang N, Zhang W, Zhao W, Guo X, Ji S
Received 15 April 2019
Accepted for publication 6 July 2019
Published 6 August 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 6297—6311
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S212355
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots (QDs) with special luminescent properties have been widely researched and applied in various fields. Thus, their release toxicity and security cannot be ignored.
Methods: In the present study, the toxicity and non-targeted metabolomics of Mn-doped ZnS QDs were investigated after single intravenous injection. Serum metabolites were evaluated based on gas chromatography–mass spectrometry together with multivariate statistical analyses [principal component analysis, partial least squares discriminant analysis, and orthogonal PLS-DA].
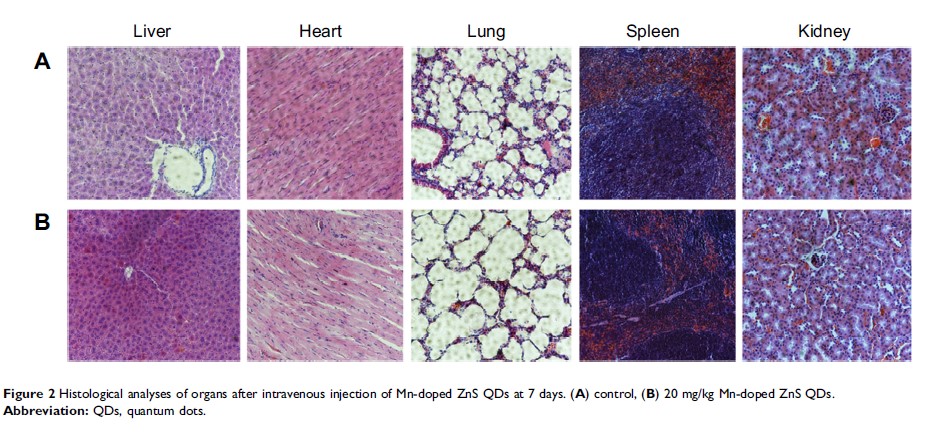
Results: The modified metabolites (variable importance in the projection (VIP) >1 and p <0.05) revealed that Mn-doped ZnS QDs exposure disturbed glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle, ketoplasia, glutaminolysis, and amino acid and lipid metabolism. The behavior, coefficients of organs, and histological changes were the same as in the control group, and the disturbance of hematology and serum biochemistry was not dose- or time-dependent.
Conclusion: Our study provides a general observation regarding the toxicity and potential metabolic responses of mice exposed to Mn-doped ZnS QDs.
Keywords: Mn-doped ZnS QDs, toxicity, metabolomics, GC-MS, mice