9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

淀粉样 β/A4 前体蛋白:复发性鼻咽癌的潜在生物标志物
Authors Li XY, Meng HL, Li KG, Yang XH, Zhu XD, Li L, Liang ZG, Pan XB, Zeng FY, Qu S
Received 1 June 2019
Accepted for publication 12 December 2019
Published 20 December 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 10651—10656
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S218030
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background and Aim: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the most common cancers in Southern China, Southeast Asia. Radiotherapy is the main treatment for NPC. Still, about 20% of patients with NPC have a recurrence. No effective serum biomarkers are available for recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma (rNPC) to date. This study aimed to explore whether amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein (APP) might serve as a valuable diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with rNPC.
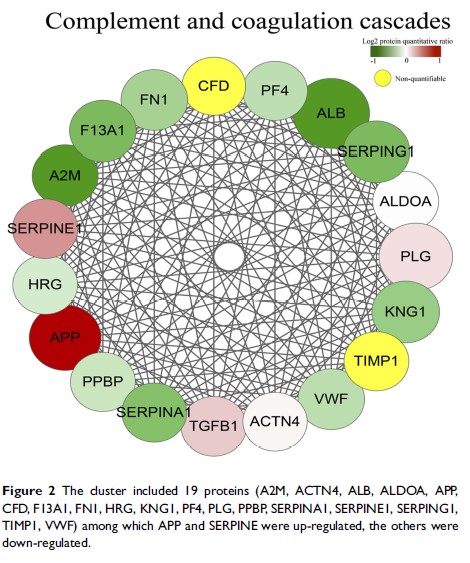
Methods: In a previous study, a tandem mass tag–based proteomic test was performed, which screened 59 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) between nonrecurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma (nrNPC) and rNPC. In this study, a protein–protein interaction was conducted to screen the key proteins among the 59 DEPs. APP was validated and evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 70 serum samples [recurrence (n = 35) and no-recurrence (n = 35)]. Also, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to evaluate the predictive value of APP.
Results: The area under the ROC curve was 0.666 (95% CI: 0.514–0.818, P = 0.044). The best cutoff point of the relative expression levels for APP was 1.23 (concentration = 16.95 ng/mL), at which the sensitivity was 55.2% and the specificity was 90.9%.
Conclusion: The findings indicated that APP might be a valuable diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with rNPC.
Keywords: amyloid beta precursor protein, biomarker, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, protein–protein interaction, recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma