9 0 5 7 8
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

Conductive polymer-based nanoparticles for laser-mediated photothermal ablation of cancer: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro evaluation
Authors Cantu T, Walsh K, Pattani VP, Moy AJ, Tunnell JW, Irvin JA, Betancourt T
Received 7 July 2016
Accepted for publication 30 October 2016
Published 16 January 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 615—632
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S116583
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Carlos Rinaldi
Abstract: Laser-mediated photothermal ablation of cancer cells aided by
photothermal agents is a promising strategy for localized, externally
controlled cancer treatment. We report the synthesis, characterization, and in
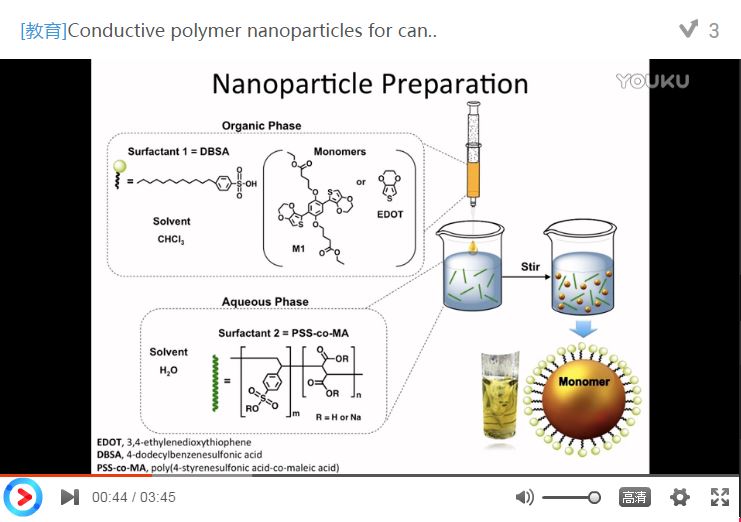
vitro evaluation of conductive polymeric nanoparticles (CPNPs) of
poly(diethyl-4,4'-{[2,5-bis(2,3-dihydrothieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxin-5-yl)-1,4-phenylene]bis(oxy)}dibutanoate)
(P1) and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) stabilized with
4-dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid and poly(4-styrenesulfonic acid-co -maleic acid) as photothermal
ablation agents. The nanoparticles were prepared by oxidative-emulsion
polymerization, yielding stable aqueous suspensions of spherical particles of
<100 nm diameter as determined by dynamic light scattering and electron
microscopy. Both types of nanoparticles show strong absorption of light in the
near infrared region, with absorption peaks at 780 nm for P1 and 750 nm for PEDOT,
as well as high photothermal conversion efficiencies (~50%), that is higher
than commercially available gold-based photothermal ablation agents. The
nanoparticles show significant photostability as determined by their ability to
achieve consistent temperatures and to maintain their morphology upon repeated
cycles of laser irradiation. In vitro studies in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
demonstrate the cytocompatibility of the CPNPs and their ability to mediate
complete cancer cell ablation upon irradiation with an 808-nm laser, thereby
establishing the potential of these systems as agents for laser-induced
photothermal therapy.
Keywords: conductive polymers, nanoparticles,
breast cancer, emulsion polymerization, nanomedicine, photothermal ablation,
PEDOT, photothermal conversion efficiency, MDA-MB-231
摘要视频链接:Conductive polymer nanoparticles for cancer ablation