108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA LINC00173 通过使海绵化 miR-765 促进 NUTF2 表达,并促使胶质瘤的肿瘤发生
Authors Du Q, Liu J, Tian D, Zhang X, Zhu J, Qiu W, Wu J
Received 12 May 2020
Accepted for publication 23 July 2020
Published 12 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 7211—7217
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S262279
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Glioma is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths. This study aimed to investigate the function and mechanism of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) LINC00173 in the regulation of glioma progression.
Methods: LINC00173 expression was measured using qRT-PCR. Survival rate was analyzed through Kaplan–Meier method. CCK8, colony formation and EdU assays were performed to measure cell proliferation while transwell was used to determine cell migration and invasion. Luciferase reporter assay was conducted to test RNA interaction.
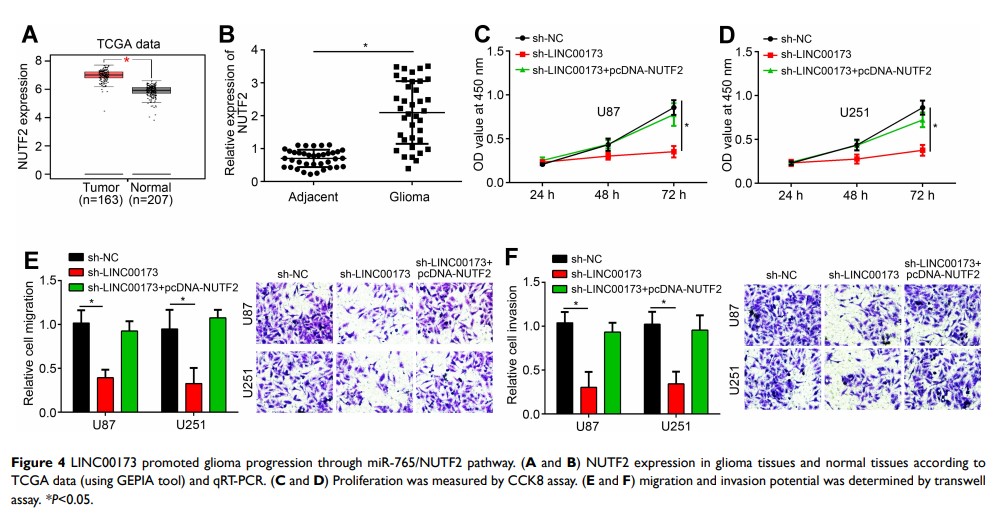
Results: LINC00173 expression was elevated in glioma tissues and cells. LINC00173 high expression predicted poor prognosis. Loss of LINC00173 inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion. LINC00173 interacted with miR-765 to enhance NUTF2 expression. MiR-765 expression was negatively correlated with LINC00173 and NUTF2 in glioma tissues. NUTF2 level was increased in glioma tissues. NUTF2 overexpression rescued the potential of proliferation, migration and invasion in LINC00173-silenced cells.
Conclusion: Our research demonstrated that LINC00173 promotes glioma progression through targeting miR-765/NUTF2 axis.
Keywords: LINC00173, miR-765, NUTF2, glioma