108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

可持续发展目标、体育和体育活动:通过体育实现与健康相关的可持续发展目标在中国的本地化:叙事回顾
Authors Dai J, Menhas R
Received 23 April 2020
Accepted for publication 28 July 2020
Published 3 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1419—1430
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S257844
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Marco Carotenuto
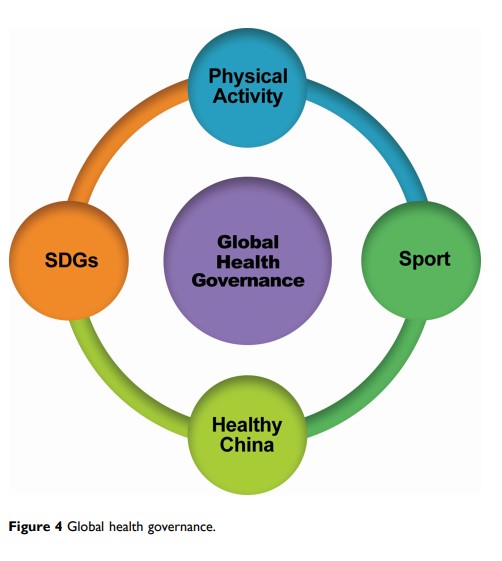
Abstract: Sport has been recognized as an essential tool for the implementation of the SDGs by The Agenda 2030 for sustainable development. The Chinese government has launched a Healthy China 2030 plan in response to the health-related SDGs. The Chinese government has introduced different kinds of measures under Healthy China 2030 plan to achieve health-related SDGs through sport and physical activity. The Healthy China program is compatible with SDGs regarding health, sport, and physical activity. After introducing the program with sustainable built environment intervention for sport and physical activity, the elderly population of China is participating in sport and physical activity to improve the national fitness level and prevent NCDs. Sport is playing a vital role in preventing NCDs in the shape of increasing physical activity among the Chinese people. Sports and physical activity play a crucial role in the implementation of health-related SDGs and further help in the achievement of “Healthy China” 2030 goal. China’s localization policies for the realization of SDGs have a global impact through glocalization in the BRI participant’s countries and supporting them to make their public health system secure and promoting global health governance.
Keywords: Healthy China, built environment, NCDs, elderly population, glocalization