110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

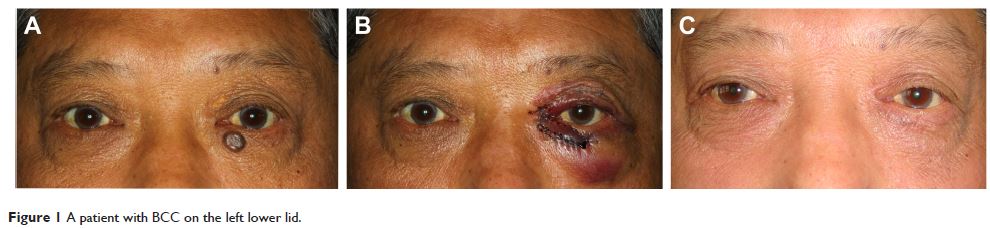
眼睑基底细胞癌:临床诊断和治疗的简要文献综述
Authors Shi Y, Jia R, Fan X
Received 15 December 2016
Accepted for publication 2 March 2017
Published 8 May 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2483—2489
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S130371
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chiung-Kuei Huang
Abstract: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a common malignant tumor throughout the
world. One of the known risk factors of BCC is intense exposure to ultraviolet
radiation. More than 50% of BCCs of the eyelid initially occur on the lower
lid. The gold standard of diagnosis of BCC is histopathology. Treatment options
for BCC consist of surgery, vismodegib, radiotherapy and imiquimod. Surgical
excision using Mohs micrographic surgery or wide surgical excision with frozen
section margin control is the first consideration for treatment of periocular
BCC. Eyelid reconstruction should be carefully considered as both function and
esthetic outcome in patients are important after clear excision of tumors.
Exenteration is considered in the case of extensive orbital invasion or
high-risk aggressive tumors in order to reduce the rate of recurrence.
Keywords: basal
cell carcinoma, eyelid, orbit, surgery, vismodegib, radiotherapy, imiquimod