110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-802 通过靶向由 cAMP 调控的磷酸化蛋白 19 抑制人喉癌细胞增殖并诱导其凋亡
Authors Ye H, Jin Q, Wang X, Li Y
Received 23 August 2019
Accepted for publication 17 December 2019
Published 20 January 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 419—430
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S228429
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background/Aims: miR-802 plays a key role in cancer progression and development. The purpose of this work is to investigate the functional role of miR-802 in laryngeal cancer and to elucidate the function of miR-802 and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein 19 (ARPP19) on laryngeal cancer.
Methods: RT-qPCR was applied to study the expression level of ARPP19 and miR-802 in the laryngeal carcinoma cell lines and tissues. CCK-8, colony formation, flow cytometry (FACS) assay were used to study the effect of ARPP19 and miR-802 on apoptosis, proliferation, and cell cycle of laryngeal carcinoma cells. Target gene prediction and luciferase reporter gene assay were applied to identify target gene of miR-802. The transcriptional mRNA and protein expression levels of ARPP19 were measured by RT-qPCR or Western blotting.
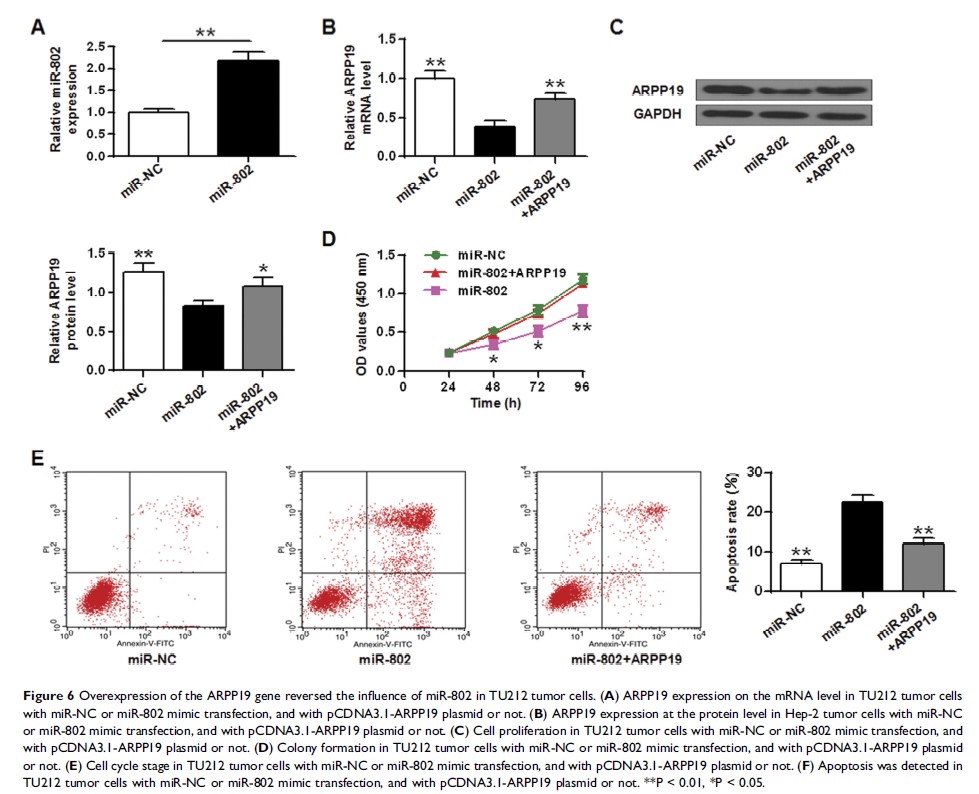
Results: miR-802 was down-regulated in laryngeal carcinoma cell lines and tissues. Laryngeal cancer cells transfected by miR-802 mimic were significantly inhibited in the terms of cell colony formation and proliferation. Furthermore, miR-802 can inhibit the expression level of ARPP19 by directly targeting the 3ʹ untranslated region (3ʹ-UTR) of ARPP19. Overexpression of the ARPP19 gene can reverse the suppressive effect of miR-802 on laryngeal cancer cells.
Conclusion: miR-802 can exert tumor suppressor effects in laryngeal carcinoma by targeting ARPP19, indicating that miR-802 protein may play a role of potential therapeutic target for clinical laryngeal cancer.
Keywords: miR-802, laryngeal carcinoma, ARPP19, proliferation, cell cycle