108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

苦参碱通过上调 LINC00472 抑制膀胱癌的细胞生长和转移
Authors Li L, Qi F, Wang K
Received 25 July 2019
Accepted for publication 8 January 2020
Published 18 February 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 1241—1251
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S224701
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Xueqiong Zhu
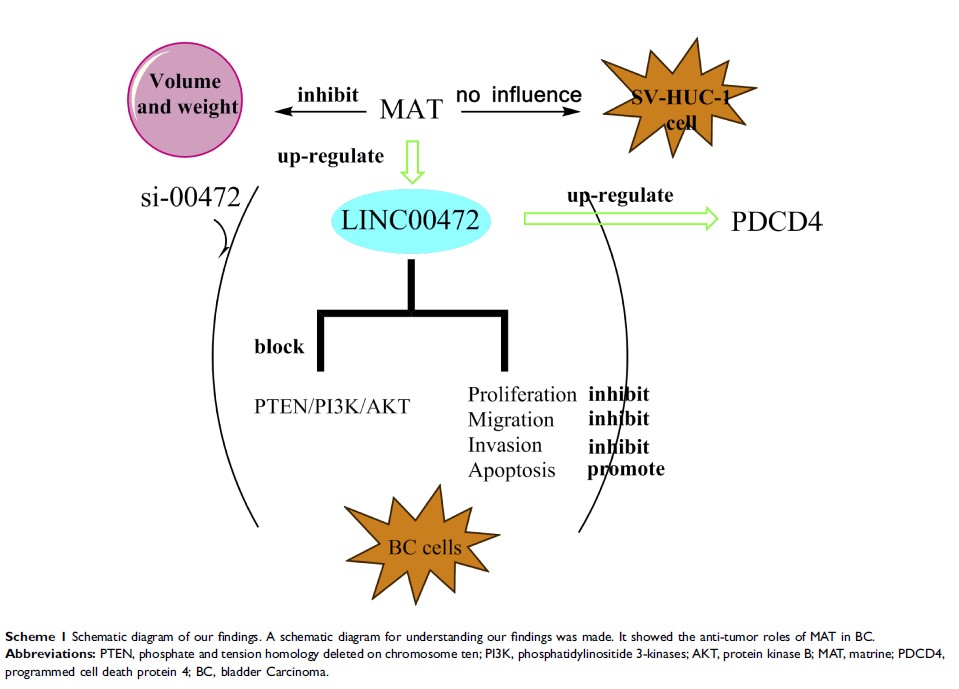
Purpose: Bladder Carcinoma (BC) is a malignant carcinoma with a high incidence in masculinity. We preliminarily researched the efficacy and mechanism of matrine (MAT) in T24 and 5637 cells.
Patients and Methods: CCK-8, flow cytometry, migration and invasion means were adopted to detect cell viability, apoptosis, migratory and invasive potentials. Moreover, LINC00472 expression was changed via transfection assays and was tested by RT-qPCR. Western blot was used for investigating the levels of CyclinD1, p53, Bcl-2, Bax, pro-Caspase-3, Cleaved-Caspase-3, β-actin, programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) and relate-proteins of cell pathways. Tumor volume and weight were tested via animal experiments.
Results: MAT could not affect the growth of SV-HUC-1 cell but MAT promoted tumor cell apoptosis but restrained viability, invasion and migration. Furthermore, LINC00472 was prominently low expressed in BC tissues. MAT positively regulated LINC00472 and transfection with si-00472 could partly reverse the efficacies of MAT. Moreover, MAT enhanced PDCD4 expression by up-regulating LINC00472. Besides, we discovered MAT elevated PTEN but restrained PI3K/AKT proteins. Finally, tumor volume and weight were declined by MAT in vivo via up-regulating LINC00472.
Conclusion: MAT restrained cell growth and metastasis but promoted PDCD4 expression by up-regulating LINC00472 via restraining PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway in BC.
Keywords: bladder carcinoma, matrine, LINC00472, PDCD4