9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA RPSAP52 上调 TGF-β1 以增加胶质母细胞瘤的癌细胞干性并预测术后存活率
Authors Wang S, Guo X, Lv W, Li Y, Zhang L, Dong C, Zhang J, Cheng G
Received 16 August 2019
Accepted for publication 11 February 2020
Published 15 April 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 2541—2547
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S227496
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Seema Singh
Introduction: Ribosomal protein SA pseudogene 52 (RPSAP52) has been characterized as an oncogenic lncRNA in pituitary tumors. Analysis of TCGA dataset revealed the upregulation of RPSAP52 in glioblastoma (GBM). We, therefore, investigated the roles of RPSAP52 in GBM.
Methods: A total of 50 GBM patients (33 males and 20 females; 54– 75 years; mean age: 61.8± 5.8 years) were selected from the 89 cases of GBM patients. Under the guidance of MRI, brain biopsy was performed to collect GBM tissues from each patient for the diagnosis of GBM. U-373 MG cells were employed and had transient transfections. qRNA, Western blot, and a series of experiments were performed to characterize their associations.
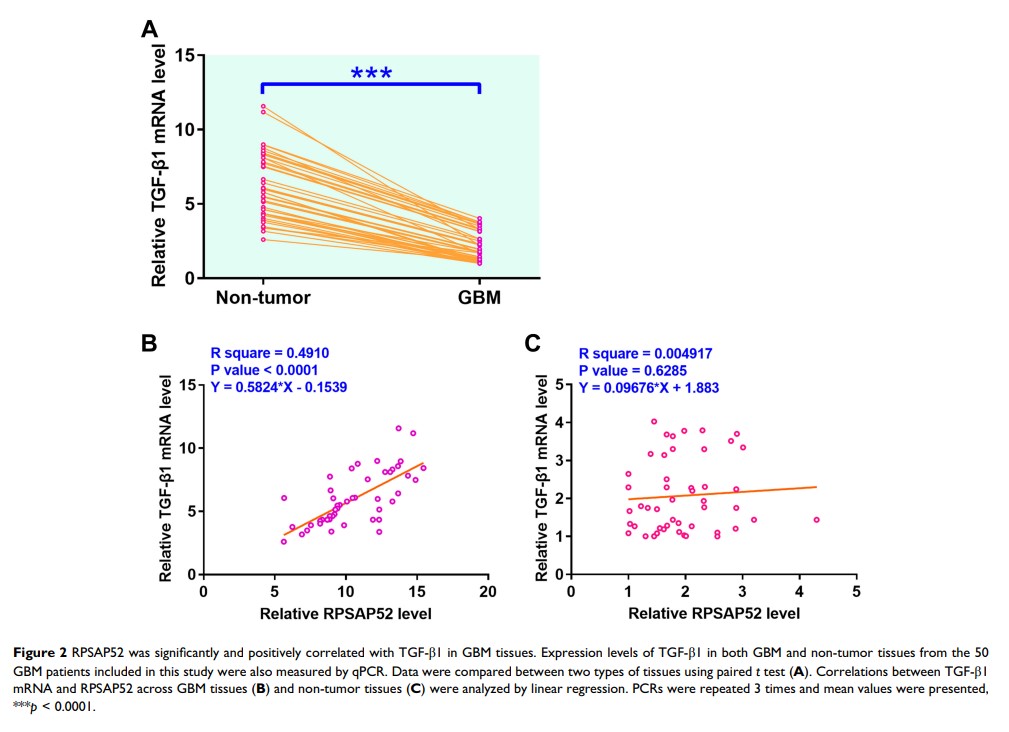
Results: The results showed that RPSAP52 was upregulated in GBM patients, and its high expression levels predicted poor survival. In GBM tissues, expression levels of RPSAP52 were significantly and positively correlated with that of TGF-β 1. In GBM tissues, RPSAP52 positively regulated the expression of TGF-β 1. Cell stemness assay showed that, compared to C and NC groups, overexpression of RPSAP52 and TGF-β 1 led to increased, while silencing of RPSAP52 led to decreased CD133+ cells. Overexpression of TGF-β 1 attenuated the effects of RPSAP52 siRNA silencing.
Conclusion: Therefore, RPSAP52 upregulates TGF-β 1 to increase cancer cell stemness and predict postoperative survival in GBM.
Keywords: glioblastoma, RPSAP52, TGF-β 1, survival, stemness