9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

二甲双胍通过下调 Cav-1 抑制丙泊酚诱导的小鼠海马神经元细胞 HT-22 的细胞凋亡
Authors Ge J, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Liu L, Gu T, Liu X, Yao L, Cai M, Sun J, Song J
Received 2 September 2019
Accepted for publication 13 December 2019
Published 21 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1561—1569
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S229520
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Objective: To elucidate the neuroprotective function of metformin in suppressing propofol-induced apoptosis of HT-22 cells.
Methods: HT-22 cells were treated with 0, 10 or 100 μmol/L propofol, followed by determination of their proliferative ability. Subsequently, changes in proliferation and apoptosis of propofol-treated HT-22 cells induced with metformin were assessed. Apoptosis-associated genes in HT-22 cells were detected by Western blot. At last, regulatory effects of Cav-1 on propofol and metformin-treated HT-22 cells were examined.
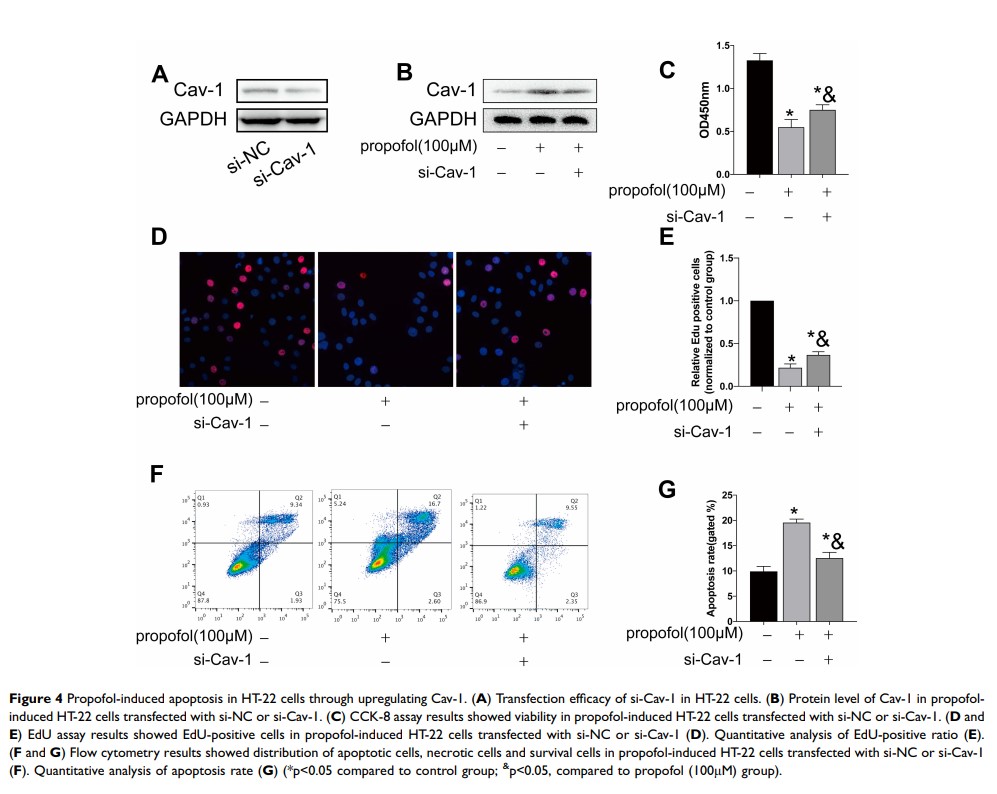
Results: Propofol treatment dose-dependently decreased proliferative ability and increased apoptosis ability in HT-22 cells, which were partially blocked by metformin administration. Upregulated Bcl-2 and downregulated Bax were observed in propofol-treated HT-22 cells following metformin administration. In addition, Cav-1 level in HT-22 cells was regulated by metformin treatment. Notably, metformin reversed propofol-induced apoptosis stimulation and proliferation decline in HT-22 cells via downregulating Cav-1.
Conclusion: In our study, we found that propofol could induce apoptosis of HT-22 cells and metformin could rescue the apoptosis effect regulated by propofol. Then, we found that metformin protects propofol-induced neuronal apoptosis via downregulating Cav-1.
Keywords: metformin, propofol, Cav-1, apoptosis