9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

Apelin-13 通过抑制自噬减轻脊髓缺血再灌注损伤的实验研究
Authors Xu Z, Li Z
Received 4 December 2019
Accepted for publication 4 March 2020
Published 22 April 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 1571—1581
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S241066
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Background: This study aimed to explore the effect of Apelin-13 in protecting rats against spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury (SCIR), as well as the related molecular mechanisms.
Methods: One week prior to the experiment, experimental Sprague–Dawley rats were injected with Apelin-13 and the autophagy activator rapamycin through the tail vein once a day for 7 consecutive days. The SCIR rat model was prepared through the abdominal aorta clamping method. At 72 h after injury, the spinal cord tissue water content, infarct volume, and normal neuron count were determined to evaluate the degree of spinal cord tissue injury in the rats. The Basso–Beattie–Bresnahan scoring standard was adopted for functional scoring of the rat hind leg, to reflect the post-injury motor function. At 72 h after injury, changes in mitochondrial membrane potential, reactive oxygen species content, and mitochondrial ATP were detected. ELISA was carried out to detect the malonaldehyde content, as well as catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione catalase activities in spinal cord tissues at 72 h after injury. Quantitative chemistry was conducted to examine the contents of nitric oxide (NO) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in spinal cord tissues. Finally, the expression of autophagy-related proteins, Beclin1, ATG5, and LC3, in spinal cord tissues was detected through the Western blotting assay.
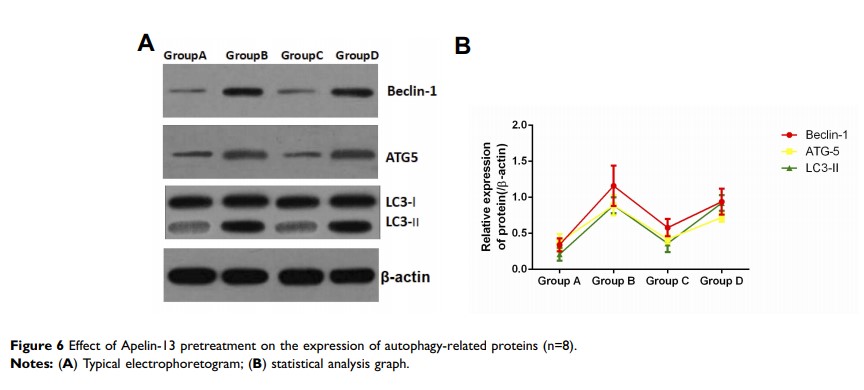
Results: Apelin-13 pretreatment alleviated SCIR, promoted motor function recovery, suppressed mitochondrial dysfunction, resisted oxidative stress, and inhibited autophagy in spinal cord tissues following ischemia reperfusion injury.
Conclusion: Apelin-3 exerts protection against SCIR by suppressing autophagy.
Keywords: Apelin-13, spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury, autophagy, rapamycin, oxidative stress, mitochondrion