9 1 2 3 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

双氢青蒿素通过抑制肿瘤微环境中巨噬细胞的极化来预防头颈部鳞状细胞癌的进展和转移
Authors Chen R, Lu X, Li Z, Sun Y, He Z, Li X
Received 9 February 2020
Accepted for publication 8 April 2020
Published 22 April 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 3375—3387
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S249046
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
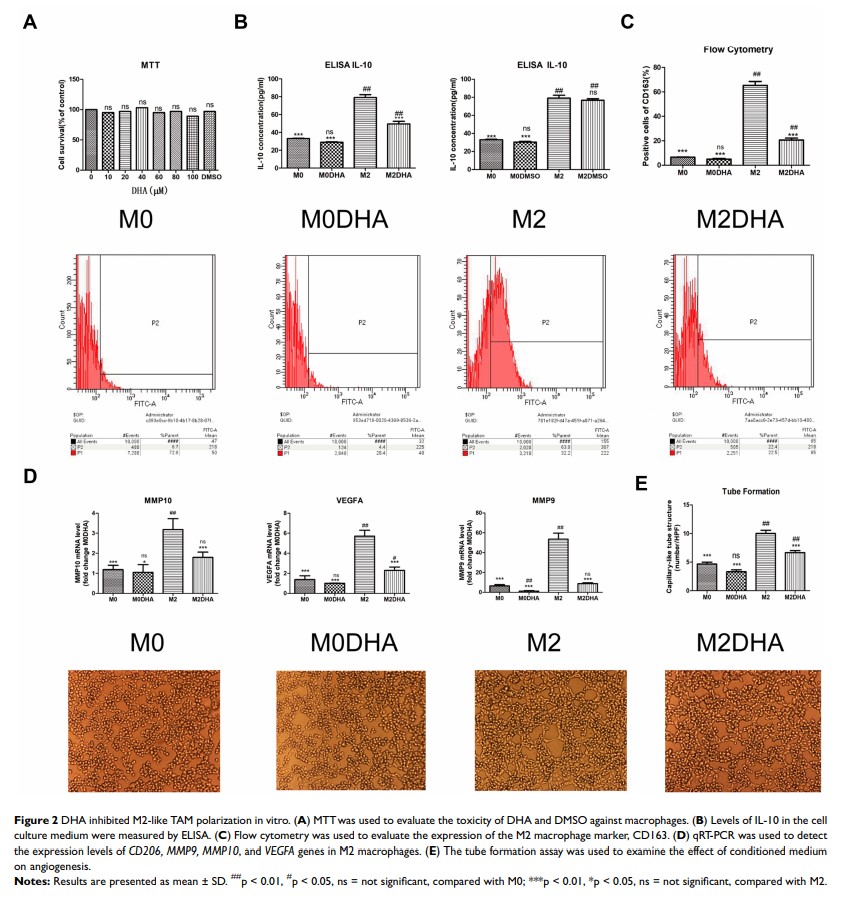
Background: Polarized M2 macrophages are an important type of tumor-associated macrophage (TAM), with roles in the growth, invasion, and migration of cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment. Dihydroartemisinin (DHA), a traditional Chinese medicine extract, has been shown to inhibit the progression and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC); however, the effect of DHA on cancer prevention, and the associated mechanism, has not been investigated in the tumor microenvironment.
Materials and Methods: First, human Thp-1 monocytes were induced and differentiated into M2 macrophages using phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-4 (IL-4). Induction success was confirmed by cell morphology evaluation, flow cytometry, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Then, DHA was applied to interfere with M2 macrophage polarization, and conditioned medium (CM), including conditioned medium from M2 macrophages (M2-CM) and conditioned medium from M2 macrophages with DHA (M2-DHA-CM), was obtained. CM was applied to Fadu or Cal-27 cells, and its effects on cancer invasion, migration, and angiogenesis were evaluated using transwell, wound-healing, and tube formation assays, respectively. Finally, Western blotting was used to evaluate the relationship between signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway activation and M2 macrophage polarization.
Results: Human Thp-1 monocytes were successfully polarized into M2-like TAMs using PMA, IL-6, and IL-4. We found that M2-like TAMs promoted the invasion, migration, and angiogenesis of HNSCC cells; however, DHA significantly inhibited IL-4/IL-6-induced M2 macrophage polarization. Additionally, as DHA induced a decrease in the number of M2-like TAMs, M2-DHA-CM inhibited the induction of invasion, migration, and angiogenesis of Fadu and Cal-27 cells. Finally, DHA inhibited M2 macrophage polarization by blocking STAT3 pathway activation in macrophages.
Conclusion: DHA inhibits the invasion, migration, and angiogenesis of HNSCC by preventing M2 macrophage polarization via blocking STAT3 phosphorylation.
Keywords: dihydroartemisinin, tumor-associated macrophages, HNSCC, STAT3, macrophage polarization