9 0 8 0 2
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用新型阳离子两亲性材料制备的胶束可增强甲氨蝶呤的经皮给药
Authors Zhao YC, Zheng HL, Wang XR, Zheng XL, Chen Y, Fei WD, Zheng YQ, Wang WX, Zheng CH
Received 26 February 2020
Accepted for publication 5 May 2020
Published 19 May 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 3539—3550
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S251431
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
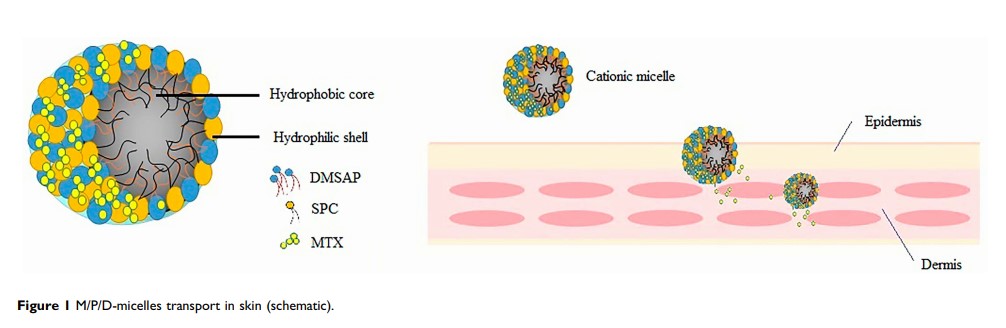
Background: Methotrexate (MTX) is an antiproliferative drug widely used to treat inflammatory diseases and autoimmune diseases. The application of percutaneous administration is hindered due to its poor transdermal penetration. To reduce side effects and enhanced percutaneous delivery of MTX, novel methotrexate (MTX)-loaded micelles prepared with a amphiphilic cationic material, N,N -dimethyl-(N′,N′ -di-stearoyl-1-ethyl)1,3-diaminopropane (DMSAP), was designed.
Materials and Methods: DMSAP was synthesized via three steps using simple chemical agents. H nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectroscopy were used to confirm the successful synthesis of DMSAP. A safe and non-toxic phosphatidylcholine, soybean phosphatidylcholine (SPC), was added to DMSAP at different ratios to form P/D-micelles. Then, MTX-entrapped micelles (M/P/D-micelles) were prepared by electrostatic adsorption. The physicochemical properties and blood stability of micelles were examined thoroughly. In addition, the transdermal potential of the micelles was evaluated by permeation experiments.
Results: In aqueous environments, DMSAP conjugates could self-assemble spontaneously into micelles with a low critical micelle concentration (CMC) of 0.056 mg/mL. Stable, spherical MTX-entrapped micelles (M/P/D-micelles) with a size of 100– 120 nm and high zeta potential of +36.26 mV were prepared. In vitro permeation studies showed that M/P/D-micelles exhibited superior skin permeability and deposition of MTX in the epidermis and dermis compared with that of free MTX.
Conclusion: These special novel cationic M/P/D-micelles can enhance the permeability of MTX and are expected to be a promising percutaneous delivery system for therapy skin diseases.
Keywords: N N -dimethyl-(N′ N′ -di-stearoyl-1-ethyl)1, 3-diaminopropane, methotrexate, micelle, percutaneous delivery