9 0 8 1 0
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 2.6 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.9 Clin Epidemiol
- 3.3 Cancer Manag Res
- 3.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.6 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.8 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.8 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 8.0 Int J Nanomed
- 2.3 Int J Women's Health
- 3.2 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 4.0 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.2 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.8 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.7 J Pain Res
- 3.3 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 4.3 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.9 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 3.5 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.5 J Inflamm Res
- 2.3 Int J Gen Med
- 4.1 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.2 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.3 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 3.3 J Multidiscip Healthc

NLCIPS:非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗预后评分
Authors Song P, Yang D, Cui X, Wang H, Si X, Zhang X, Zhang L
Received 12 April 2020
Accepted for publication 25 June 2020
Published 17 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5975—5985
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S257967
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
Introduction: Currently in China, many immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have been approved for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Some patients can not benefit from ICIs, and approximately 50% of patients have immunotherapy-related toxicity. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor carefully the selection of immunotherapy population using biomarkers to maximize the benefit of patients with NSCLC.
Methods: A prospective analysis was performed on patients with advanced NSCLC who were treated with ICIS at our hospital from March 2018 to June 2019, up to the follow-up deadline of December 31, 2019. The primary end points were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS), and the secondary end points were objective response rate and disease control rate. A lasso regression was used for the univariate analysis, and Cox regression analysis was used for the multivariate analysis. An efficacy prediction line chart was developed.
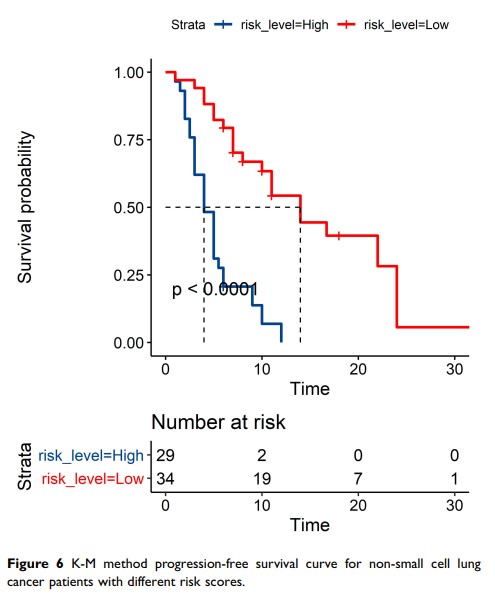
Results: A total of 63 patients were included in the study. The median PFS was 7.0 months (95% CI, 5.0– 11.0) and did not reach the median OS. According to the lasso regression, significant univariate factors were smoking index, PD-ligand 1 expression, and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR). According to the multivariate analysis, the Cox proportional hazards model showed that smoking index and NLR are independent predictors of PFS in immunotherapy. A model comprised of independent predictors was developed based on a multivariate logical analysis of the main cohort—non-small cell lung cancer immunotherapy prognosis score. This model is shown as a nomogram with a C-index of 0.801 (95% CI, 0.744, 0.858), which has high prediction accuracy.
Conclusion: This predictive model, including NLR and smoking index, can achieve a 1-year PFS in immunotherapy of patients. PD-1 inhibitors have been demonstrated to be effective and safe in the clinical treatment of patients with NSCLC.
Keywords: immunotherapy, prognosis score, non-small cell lung cancer, smoking index